Author : Haya Assem
What Is A Profit And Loss Statement In Business: A Complete Guide

Table of contents:
- Key Takeaways
- What Is A Profit And Loss Statement?
- What Is The Purpose Of A P&L Statement In Business?
- What Is Included In A Profit And Loss Statement
- How to Make a Profit and Loss Statement
- Profit And Loss Statement Example
- Common Profit And Loss Statement Errors To Avoid
- How To Analyze Profit And Loss Statement
- Accrual Vs Cash Basis Accounting Impact On P&L
- Profit and Loss Statement vs Balance Sheet
- Automate P&L Statement with Enerpize
- FAQs
A profit and loss statement, also known as a P&L statement or income statement, is a key financial report that summarizes your business’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period. Understanding what a profit and loss statement is and how it works is essential for making informed business decisions, managing costs, and planning for growth.
This article covers everything from components to how to read a profit and loss statement, along with practical tips, examples, and automation tools.
Key Takeaways
- A profit and loss statement summarizes revenues, expenses, and net profit over a specific period.
- What is included in a profit and loss statement: revenue, COGS, operating expenses, other income, taxes, and net income.
- How to make a profit and loss statement: gather data, calculate gross profit, subtract expenses, and compute net profit.
- Profit and loss statement vs balance sheet: P&L shows performance over time; the balance sheet shows financial position at a point in time.
- Accrual vs cash basis accounting impact on P&L: affects when revenue and expenses are recorded.
- Common P&L statement errors to avoid are misclassifications, missing revenue, ignoring COGS adjustments, and outdated data.
- How to analyze profit and loss statement: review revenue trends, gross and net profit margins, operating expenses, and ratios.
What Is A Profit And Loss Statement?
A profit and loss statement summarizes a company’s revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period, monthly, quarterly, or annually. Its main purpose is to show whether the business generated a profit or incurred a loss.
A business profit and loss statement is more than just a list of numbers; it provides insights into financial performance, cost management, and operational efficiency.
What Is The Purpose Of A P&L Statement In Business?
The purpose of a profit and loss (P&L) statement in business is to provide a clear summary of a company’s revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period of time, typically a month, quarter, or year. It helps businesses understand whether they are profitable or operating at a loss and offers insights into the financial health of the business.
Evaluate Financial Performance
A P&L statement allows you to measure how efficiently your business generates profit from its operations. Comparing current results with past periods helps identify performance trends and areas for improvement.
Manage Expenses Effectively
By analyzing operating and non-operating expenses, businesses can identify unnecessary spending and control costs.
Support Decision-Making
Business owners and managers use P&L statements to decide on pricing, cost control, and investment strategies. It helps determine if the business can expand, reduce expenses, or adjust operations.
Meet Reporting and Compliance Needs
A P&L statement is often required for financial reporting, tax filing, and securing loans or investments. It demonstrates transparency and credibility to stakeholders.
Note: Enerpize Accounting Software automates P&L reporting by collecting all revenue and expense data in one place, generating accurate and easy-to-read statements, and enabling real-time insights for smarter business decisions.
What Is Included In A Profit And Loss Statement
A Profit and Loss statement is more than just numbers on a page; it’s an overview of your business’s financial health. It shows how much money your business earns, spends, and ultimately keeps as profit over a specific period.
A P&L statement usually includes:
- Revenue/Sales: The total income from selling products or services. This is the starting point of your P&L.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs tied to producing or delivering your products, such as materials, labor, or manufacturing expenses.
- Gross Profit: Revenue minus COGS, showing how much money is left before covering operating expenses.
- Operating Expenses: Day-to-day costs of running your business, including rent, salaries, utilities, marketing, and office supplies.
- Operating Profit (EBIT): Profit from your core operations after subtracting operating expenses from gross profit.
- Other Income and Expenses: Non-operational items, like investment gains, interest, or one-time expenses.
- Taxes: The amount owed in income tax based on your profits.
- Net Profit / Net Income: The bottom line that shows what your business actually earns after all expenses and taxes.
Note: Enerpize Accounting Software automatically categorizes revenues, COGS, and expenses, making it easy to generate a profit and loss statement for a small business or large enterprises in minutes.
How to Make a Profit and Loss Statement
Creating a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement doesn’t have to be complicated. It’s all about organizing your revenue, expenses, and profits in a clear, structured way. Here are the detailed steps:

1- Gather Your Financial Data
Start by collecting all your financial records for the reporting period. This includes sales invoices, receipts, bank statements, payroll records, and any other documents related to income and expenses.
2- List Your Revenue
Revenue, or total sales, is the starting point of your P&L statement. Include all income generated from selling products or services. Make sure to separate different revenue if your business has multiple products or services< for a clearer earnings picture.
3- Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS represents all the direct costs of producing or delivering your products or services. This includes raw materials, manufacturing labor, and any other costs directly tied to making your product. Subtracting COGS from revenue helps determine your gross profit, which shows how efficiently your business produces and sells its offerings.
Learn more about how to calculate COGS in our detailed guide on: How to Calculate Cost of Goods Sold.
4- Determine Gross Profit
Gross profit is calculated by subtracting COGS from total revenue. This figure shows how much money your business retains before paying operational costs. A high gross profit margin often indicates strong pricing strategies or efficient production processes.
5- Add Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the day-to-day costs required to run your business. These include salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, insurance, and office supplies. Tracking these expenses helps you identify areas where you can reduce costs and improve profitability.
6- Include Other Income or Expenses
Other income or expenses are items not directly related to your main business operations. Examples include investment income, interest earned, gains or losses from selling assets, or one-time expenses.
7- Subtract Taxes
Taxes owed on your profits must be deducted to calculate your net profit. This ensures the P&L reflects the accurate amount of money your business keeps after fulfilling its tax obligations.
8- Calculate Net Profit
Net profit, also called net income, is the final figure after subtracting all expenses and taxes from revenue. This is the ultimate indicator of business success, showing whether your company is profitable and by how much.
Note: To save time and ensure accuracy, use the Enerpize Profit and Loss Statement Template. This helps you organize all data neatly and prevents calculation errors.
You might also find this helpful: How To Prepare An Income Statement
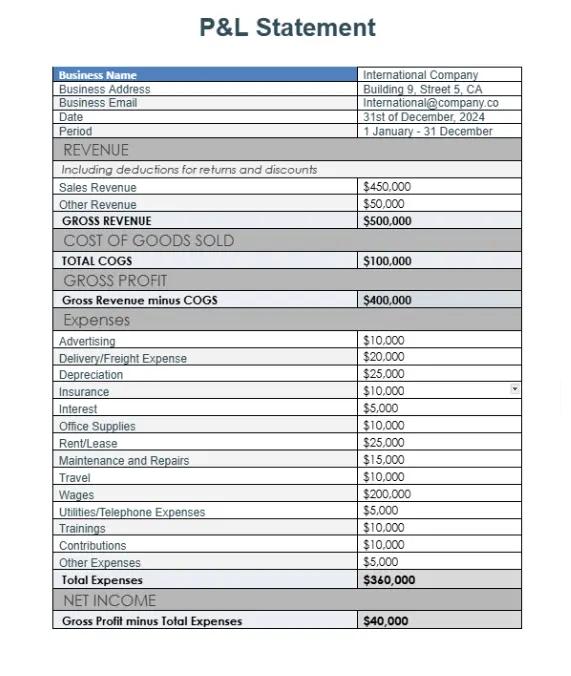
Profit And Loss Statement Example
A Profit and Loss (P&L) statement summarizes a company’s revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period to show its net profit or loss. Below is a simple example to illustrate how a P&L statement is structured.
Example for the International Company for the Year Ended December 31, 2024: This P&L statement summary demonstrates the company’s financial performance over the year.
Common Profit And Loss Statement Errors To Avoid
Creating a P&L statement may seem straightforward, but small mistakes can lead to inaccurate financial reporting. Here are the most common P&L statement errors to avoid:
- Mixing Personal and Business Expenses: Including personal expenses in your business P&L can distort your profit. Always separate business costs from personal spending.
- Incorrect Classification of Expenses: Misclassifying operating vs. non-operating expenses (e.g., treating interest expense as operating) can misrepresent profitability.
- Not Including All Revenue Sources: Missing revenue streams (like service income or other one-time sales) will understate total income.
- Ignoring COGS Adjustments: Failing to account for inventory changes, returns, or discounts can lead to inaccurate gross profit.
- Overlooking Accruals or Prepayments: Failing to account for prepaid expenses, deferred revenue, or accrued expenses can distort net profit.
- Math or Data Entry Errors: Simple addition or subtraction mistakes can throw off totals and net profit.
- Failing to Update the Statement Regularly: Using outdated data can make your P&L irrelevant for decision-making.
How To Analyze Profit And Loss Statement
After preparing your profit and loss statement, the next step is to interpret what the figures reveal about your business’s performance. Analyzing the P&L helps you move beyond raw numbers to understand revenue patterns, cost behavior, and profitability trends over time.
Here’s how you can break down and evaluate each part of your statement to gain meaningful financial insights:
1- Review Revenue Trends
Start by examining total revenue and comparing it over multiple periods, monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Identify which income sources are growing or declining to understand your business’s sales performance.
2- Examine Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Analyze your COGS to see how much it costs to produce or purchase goods. A rising COGS without a matching increase in revenue can reduce profit margins.
3- Assess Gross Profit Margin
Use the formula Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue – COGS) ÷ Revenue × 100 to determine how efficiently your business produces goods or delivers services. A declining margin may indicate higher costs or lower pricing.
4- Analyze Operating Expenses
Review your operating expenses, such as rent, salaries, and utilities, to ensure they align with revenue. Identify where you can cut costs or improve efficiency.
5- Evaluate Operating Profit (EBIT)
Operating profit (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) reflects how much your core operations earn before financial or tax adjustments. Compare it across periods to gauge operational efficiency.
6- Review Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Check for any additional income (like interest or asset sales) and expenses (such as loan interest or one-time losses) that affect your net profit. This helps distinguish regular performance from unusual items.
7- Assess Net Profit Margin
Calculate Net Profit Margin = Net Profit ÷ Revenue × 100 to understand your overall profitability after all costs and taxes. Compare this margin with industry standards to evaluate competitiveness.
8- Perform Ratio and Trend Analysis
Use ratios such as expense-to-revenue, gross margin, and net margin to compare performance over time. Trend analysis helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and growth opportunities.
Accrual Vs Cash Basis Accounting Impact On P&L
The way you record your business income and expenses, using either the accrual basis or the cash basis, has a direct impact on how your profit and loss statement reflects financial performance.
1- Cash Basis Accounting
Under the cash basis, revenues and expenses are recorded only when cash actually changes hands. This method gives a straightforward view of your cash flow. However, it might not accurately represent profitability if payments are delayed. Cash basis is usually suited to small businesses or sole proprietors who prioritize tracking cash flow over long-term performance trends.
How transactions are recorded:
- Revenue is recognized when payment is received from customers.
- Expenses are recorded when you pay suppliers or bills.
For example, if you made a $5,000 sale in December but received payment in January, that income will appear in January’s P&L, not December’s.
2- Accrual Basis Accounting
Under the accrual basis, revenues and expenses are recorded when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid. This method is best for businesses that deal with invoices, credit sales, or long-term contracts and need a clearer view of ongoing performance. This method provides a more accurate picture of profitability over time, since it matches income and expenses to the period they relate to.
How transactions are recorded:
- Revenue is recognized once a product or service is delivered, even if payment comes later.
- Expenses are recorded when they happen, not when they are paid.
For example, if you made a $5,000 sale in December and got paid in January, the income still appears in December’s P&L, showing when the business truly earned it.
Profit and Loss Statement vs Balance Sheet
Both the profit and loss statement and the balance sheet are essential financial statements that provide insights into a company’s financial health. However, they serve different purposes and present information from different perspectives.
| Perspective | Profit and Loss Statement | Balance Sheet |
| Purpose | Shows the company’s performance over a specific period (monthly, quarterly, or annually) by summarizing revenues, expenses, and net profit or loss. It tells how much money the business makes or loses during this period. | Presents the company’s financial position at a specific date, showing assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity. It identifies what the business owns and owes right now. |
| Time Frame | Covers a period of time (e.g., January 1 – December 31). | Reflects a snapshot of the company’s financial position on a specific date (e.g., December 31). |
| What It Indicates | Measures profitability and operational efficiency. | Measures financial stability and liquidity. |
| Relationship | The net profit from the P&L flows into the equity section of the balance sheet as retained earnings. | Reflects the cumulative effect of profits or losses reported in the P&L over time. |
To understand this relationship in detail, check out our comprehensive comparison of Income Statement vs Cash Flow Statement, which highlights how these statements differ and why each matters.
Note: Enerpize automatically generates both the Profit and Loss Statement and the Balance Sheet in real time. It tracks revenues, expenses, and assets accurately, allowing you to assess profitability and financial health side by side, without manual calculations.
Automate P&L Statement with Enerpize
Enerpize is a comprehensive accounting and business management software designed to simplify financial operations for businesses of all sizes. From tracking sales and expenses to generating financial statements, Enerpize online accounting software centralizes all your accounting processes in one platform. With automation, real-time insights, and seamless reporting, managing your business finances becomes easier, faster, and more accurate.
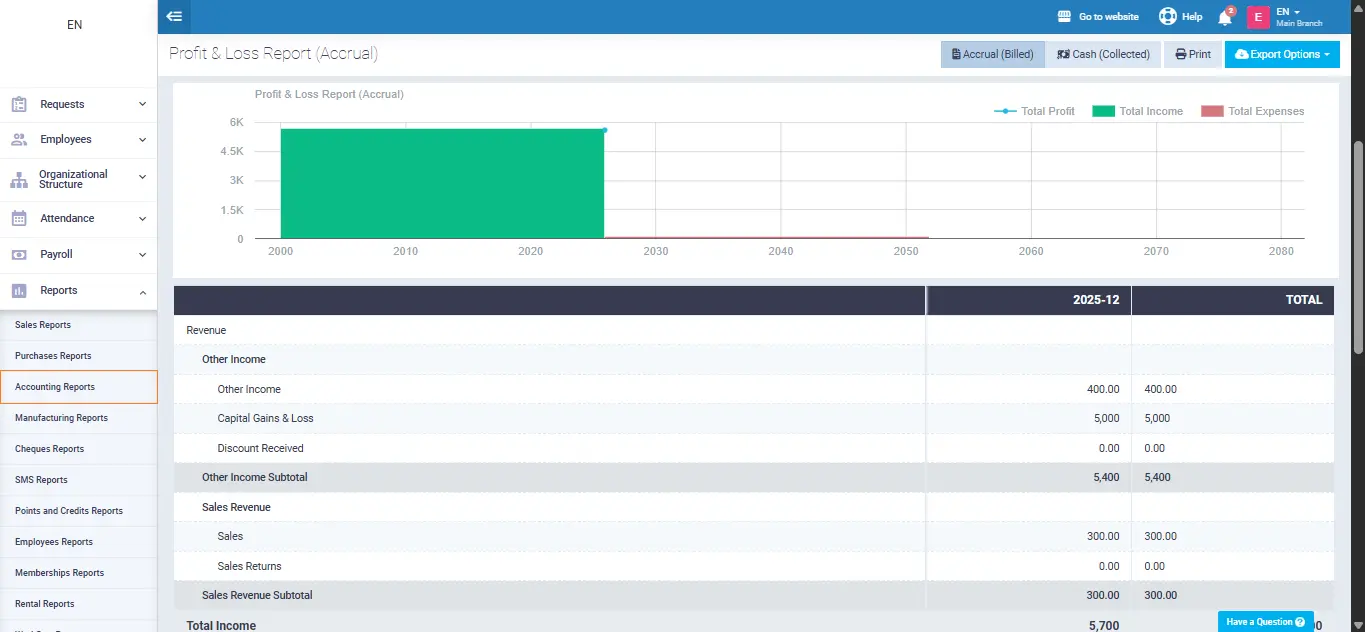
Creating a profit and loss statement manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Enerpize streamlines the process of creating profit and loss statement to avoid manual errors, allowing you to focus on making informed business decisions rather than crunching numbers.
- Real-Time Tracking: Enerpize automatically records all your revenues and expenses as they happen. Whether it’s sales, invoices, or payments, your P&L statement stays up to date without manual entry.
- Smart Categorization: Every transaction is categorized correctly, including cost of goods sold, operating expenses, or other income, so you get a clear picture of your business performance immediately.
- Automatic Calculations: Gross profit, operating profit, and net profit are calculated instantly. No formulas, no spreadsheets, Enerpize handles it all.
- Flexible Reporting: Generate P&L statements for any period, monthly, quarterly, or yearly, with just a click. Compare periods easily to track growth, spot trends, and make informed decisions.
- Seamless Integration: Your net profit or loss is automatically reflected in your Balance Sheet under retained earnings. Enerpize keeps all your financial statements accurate and in sync.
FAQs
Is an income statement the same as a profit and loss?
Yes. The income statement and the profit and loss (P&L) statement are the same. Both summarize revenues, expenses, and net profit or loss over a specific period.
What does a profit and loss statement show?
A P&L statement shows your business’s financial performance, including total revenue, expenses, and net profit or loss, helping you understand profitability and make informed decisions.
How to calculate net income from a P&L?
Net income is calculated by subtracting total expenses (including COGS and operating costs) from total revenue:
Net Income = Total Revenue − Total Expenses
How does the P&L statement relate to the cash flow statement?
The P&L statement shows profit or loss, while the cash flow statement tracks actual cash inflows and outflows. Net income from the P&L is the starting point for preparing the cash flow statement.
How to create a P&L statement for my startup?
To create a P&L statement:
- List all sources of revenue.
- Record all expenses, including COGS and operating costs.
- Subtract total expenses from total revenue to calculate net income.
Creating P&L statements is easy with Enerpize.
Try Enerpize accounting software to create your statements automatically.