Author : Haya Assem
Reviewed By : Enerpize Team
Balance Sheet for Small Business: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of contents:
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Balance Sheet?
- Importance of Balance Sheet for Small Business
- Main Components of Basic Balance Sheet
- What Is the Balance Sheet Equation?
- How To Make a Balance Sheet for Businesses
- Balance Sheet Template for Small Business
- Balance Sheet Example for Small Businesses
- How To Read a Balance Sheet?
- What Does a Balance Sheet Tell You?
- How to Prepare a Balance Sheet from an Income Statement?
- Similarities Between Balance Sheet and Income Statement
- Automate Balance Sheet Generation With Enerpize
- FAQs about Balance Sheets
Managing and maintaining a company’s financial stability can often be burdensome. Keeping the inflow and outflow of cash in balance, maintaining assets and liabilities, and assuring the company’s financial health is a real challenge that leaves many small business owners perplexed about their company’s financial status. An accurately organized balance sheet can put an end to this perplexity. Creating a clear, comprehensive, and informative balance sheet for small businesses is a common dilemma that many entrepreneurs often face.
But fret not: we’ll guide you through the whole process of creating a balance sheet, simplifying any complexities, and equipping you with all the knowledge and skills that you need to build a strong balance sheet that will help you keep your finances under control.
The following paragraphs will break down the complexity by explaining what a balance sheet, its importance, and its vital role is in helping guide your small business toward financial stability and success.
Key Takeaways
- A balance sheet is a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific time, showing what it owns (assets), owes (liabilities), and the owner's equity, which helps assess financial health and business performance.
- For small businesses, a balance sheet is essential for understanding whether assets outweigh liabilities, which signals financial stability. It also supports better decision-making, tax planning, and investor or lender trust.
- It helps track liquidity by showing how much cash or easily convertible assets a business has available to cover daily operations, bills, or new opportunities.
- The balance sheet also reveals debt levels and repayment responsibilities, helping owners manage liabilities more effectively and avoid overextending.
- Over time, comparing balance sheets lets businesses track growth by monitoring changes in assets, liabilities, and equity across different periods.
- The main components, assets, liabilities, and equity, must balance using the formula: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. This ensures accurate and consistent financial reporting.
- Reading and understanding a balance sheet helps business owners interpret their company’s financial position accurately, identify strengths and risks, and make data-driven financial decisions.
What is a Balance Sheet?
A balance sheet is a financial report that shows a company's financial status at a certain point in time, often at the end of an accounting period, such as a quarter or a year. It is the main financial statement used by companies, investors, and analysts to measure a company's financial health and business performance.
The balance sheet is commonly referred to as the "Statement of Financial Position" because it highlights the company's owns (assets), its owes (liabilities), and the ownership interest (equity) of the owners or shareholders making it essential for Banks and investors to examine the balance sheet to have a better understanding of your company's financial health before investing in it or lending you money.
Importance of Balance Sheet for Small Business
Its value comes from the vital insights it provides and the different ways in which it might help a business. It gives a snapshot of the company's financial health at a certain point in time by indicating if the company has more assets than liabilities, which is a key indication of financial stability. It assists potential investors and lenders in evaluating liquidity, debt management, and tax planning, while building trust. In conclusion, the balance sheet is a critical tool for assessing financial health, making informed decisions, and contributing to a company's overall success and sustainability.
Financial Health Assessment
A balance sheet for a small business helps determine the company’s financial health, so, small business owners and stakeholders can decide whether the company's assets outnumber its liabilities, which is an important measure of financial stability.
Liquidity Management
It assists in evaluating a company's liquidity and keeping the business owner aware of the amount of cash and assets that can be easily converted into cash. Being aware of this information will help you complete your daily operations, pay bills, and seize opportunities.
Read Also: Liquid Assets Formula: A Comprehensive Guide
Debt Management
Small businesses often rely on loans and credit to finance their operations. While a balance sheet shows the scope of a company's liabilities, helping owners in managing and planning for debt repayment.
Investor and Lender Confidence
Investors and lenders usually seek a copy of the company's current balance sheet for the period in order to understand the company's financial status and determine if the company is suitable as an investment choice. So, that’s why a well-organized balance sheet matters.
Track Business Growth
Small business owners can track their company's growth and see how assets and equity have evolved over time by comparing balance sheets from different periods.
Tax Planning
A balance sheet helps with tax preparation by giving information about the company's assets and liabilities. This data can aid in optimizing tax strategies and deductions.
Main Components of Basic Balance Sheet
1- Assets
This section lists all the resources and properties that a company owns, including cash, accounts receivable, inventory, real estate, equipment, and investments. Assets can be further classified as follows:
- Current Assets: Assets that can be quickly turned into cash in a year or less. The current assets may include cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, accounts receivable, inventory, supplies, etc....
- Long-term assets: Long-term assets are those a company intends to hold for more than a year. These can include:
- Fixed Assets such as Property, Buildings, Land, and Machinery.
- Intangible Assets such as Software, licenses, trademarks, patents, and copyrights.
2- Liabilities
Liabilities represent the company's obligations or debts, including accounts payable, loans, and accrued expenses. Liabilities are further classified into two types:
- Current Liabilities: Under current liabilities come accounts payable, short-term loans, trade payables, and outstanding dues.
- Non-Current Liabilities: Any debts or other financial commitments that can be paid after a year are examples of non-current liabilities such as bonds, long-term debts, debentures, and mortgage loans.
3- Equity
Equity, also known as shareholders' equity or owner's equity, is the remaining interest in the assets of the company after deducting its liabilities. It indicates the ownership stake of the company's shareholders.
4- Retained earnings
It is the amount of a company's profits that are reinvested in the business rather than distributed to shareholders as dividends.
Read Also: How to Calculate Retained Earnings on A Balance Sheet
5- Shareholders' equity
This is the amount of capital that a company receives for its business operations.

Recommended for you: Opening Entries in Accounting: Definition & Examples
What Is the Balance Sheet Equation?
The balance sheet equation, commonly referred to as the balance sheet formula, is a basic accounting concept that shows the connection between a company's assets, liabilities, and equity. It is formatted as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This equation assures that a balance sheet is always in balance since assets must equal the total liabilities and equity. A balance sheet is a vital tool for assessing a company's financial health, liquidity, and overall financial performance. It is often included in a company's financial statements, along with the income and cash flow statements, providing an extensive overview of the company's financial status.
Read Also: Comparative Balance Sheet: A Comprehensive Guide
How To Make a Balance Sheet for Businesses
1- Specify a period/date
A balance sheet is usually created per specific period, it is commonly created quarterly which is normally due on the last day of March, June, September, and December. Other companies may also do a monthly balance sheet.
2- Collect Financial info
Once you’ve set your date, make sure to gather all needed financial data, such as assets, liabilities, transactions, invoices, and financial statements of the company throughout your specified period. It's better to sort them by liquidity. So, start by listing the company’s current assets then include the long-term assets.
3- List the Assets
List your company's assets in the assets column and don’t forget to include both current and non-current (Long-term) assets. Add up all current and non-current assets under the total assets, compare them with your general ledger, and settle any differences.
4- Determine Liabilities
List the company’s owes (liabilities), including both current and non-current liabilities.
Calculate the total for each, then add the current liabilities subtotal to the long term liabilities to get the final amount. Label this total as ‘Total Liabilities’.
Read Also: How to Calculate Liabilities
5- Calculate Shareholders’ Equity
Determining shareholders’ equity in a small business is usually easy because it most likely has a single owner, but it is an essential step to include it. Then add it up with the liabilities and compare it with the assets’ total (Total Liabilities + Total Shareholders’ Equity = Total Assets).
Note: It’s highly expected that not both sides will equal each other, but in this state, you’ll need to go back to your general ledger and review it.
Balance Sheet Template for Small Business
Want to get a ready-to-use balance sheet? Download a free balance sheet template.

Balance Sheet Example for Small Businesses
A well-organized balance sheet is essential for small business owners who want to monitor their financial health and make informed decisions. It not only keeps track of your assets, liabilities, and equity but it may also be used to manage growth and plan for future investments or loans.
The following is an example of a small business balance sheet, demonstrating how financial data could be structured to provide a clear picture of the business's current financial status:
| Item | Amount |
| Asset | |
| Current Assets | |
| Cash | $30,000 |
| Account Receivable | $15,000 |
| Inventory | $25,000 |
| Prepaid Expenses | $5,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $75,000 |
| Non-Current Assets | |
| Equipment | $50,000 |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation | ($10,000) |
| Total Non-Current Assets | $40,000 |
| Total Assets | $115,000 |
| Liability | |
| Current Liabilities | |
| Accounts Payable | $20,000 |
| Short-Term Loans | $10,000 |
| Accrued Expenses | $5,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $35,000 |
| Non-Current Liabilities | |
| Long-term Debt | $30,000 |
| Total Non-Current Liabilities | $30,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $65,000 |
| Owner’s Equity | |
| Owner’s Capital | $40,000 |
| Retained Earnings | $10,000 |
| Total Owner’s Equity | $50,000 |
How To Read a Balance Sheet?
To effectively read a balance sheet, you need to understand the three primary sections: assets, liabilities, and equity. Each section provides insights into the company’s financial state.
The following example balance sheet breakdown illustrates how each item fits into these categories and how the totals balance according to accounting standards.
1- Assets ($115,000 Total)
Assets represent everything the business owns that has value or will bring future economic benefit.
- Current Assets ($75,000): These are short-term assets expected to be converted into cash or used within one year.
- Cash ($30,000): The available money the business holds in hand or in bank accounts. It’s the most liquid asset.
- Accounts Receivable ($15,000): The amount customers owe for goods or services already delivered. It shows expected incoming cash.
- Inventory ($25,000): The cost of goods available for sale or raw materials to be used in production.
- Prepaid Expenses ($5,000): Payments made in advance for services (like rent or insurance) that will benefit future periods.
Total Current Assets = $75,000
- Non-Current Assets ($40,000): These are long-term resources that provide value over time (usually more than one year).
- Equipment ($50,000): Long-term assets used in daily operations, such as machinery or computers.
- Less: Accumulated Depreciation ($10,000): Represents the total wear and tear or usage cost deducted over time.
Total Non-Current Assets = $50,000 - $10,000 = $40,000
Total Assets = $75,000 (Current) + $40,000 (Non-Current) = $115,000
2- Liabilities ($65,000 Total)
Liabilities are the company’s debts or obligations that it owes to others.
- Current Liabilities ($35,000): Debts due within one year.
- Accounts Payable ($20,000): Money owed to suppliers for goods or services purchased on credit.
- Short-Term Loans ($10,000): Loans that must be repaid within a year, often used to cover immediate expenses.
- Accrued Expenses ($5,000): Expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid, such as wages or utilities.
Total Current Liabilities = $35,000
- Non-Current Liabilities ($30,000): Obligations that are not due within a year.
- Long-Term Debt ($30,000): Loans or financial obligations due after more than one year, such as bank loans or bonds.
Total Non-Current Liabilities = $30,000
Total Liabilities = $35,000 (Current) + $30,000 (Non-Current) = $65,000
3- Owner’s Equity ($50,000 Total)
Owner’s equity represents the owner’s claim on the business after all liabilities are paid, essentially, what the business is worth to the owner.
- Owner’s Capital ($40,000): The money the owner initially invested in the business.
- Retained Earnings ($10,000): Profits that have been kept in the business instead of being withdrawn by the owner.
Total Owner’s Equity = $40,000 + $10,000 = $50,000
Verification: The Accounting Equation
This example complies with the accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This ensures that the company's balance sheet is balanced. In the balance sheet provided, the total assets amount is $115,000, while the total liabilities are $65,000, and the total owner's equity is $50,000. According to the equation, assets must equal the sum of liabilities and equity.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
115,000=65,000+50,000
Read Also: What is Accounts Receivable Turnover?
What Does a Balance Sheet Tell You?
A balance sheet gives business owners valuable insights into their company’s overall financial health and stability at a specific point in time. By examining the relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity, you can understand how well your business is managing its resources, debts, and growth potential.
A balance sheet reveals the following:
Liquidity and Short-Term Stability
With current assets of $75,000 and current liabilities of $35,000, the business can comfortably cover its short-term obligations. The current ratio (Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities) is 2.14, meaning the company has more than twice the assets needed to pay short-term debts, a strong liquidity position.
Financial Obligation Analysis
The total liabilities are $65,000, while the owner’s equity is $50,000. This indicates that the business relies slightly more on external financing than on the owner’s investment. A debt-to-equity ratio of 1.3 ($65,000 ÷ $50,000) suggests moderate leverage, manageable but worth monitoring.
Asset Management
The business owns $115,000 in total assets, with a significant portion ($40,000) in long-term assets like equipment. This shows resource stability, supporting both daily operations and long-term productivity.
Owner’s Equity Position
After settling all liabilities ($65,000), the owner still retains $50,000 in equity, showing that the company has built solid net value over time.
Earnings Retention and Growth
The retained earnings of $10,000 indicate that the business is generating profits and reinvesting them rather than distributing all of them to the owner, an indicator of sustainable growth.
How to Prepare a Balance Sheet from an Income Statement?
In any business, a balance sheet and an income statement indicate clear financial accounting facts. They both follow the same accounting cycle, starting with the income statement and followed by the balance sheet. The key connection between the two statements is that the profit generated from the income statement is added to the balance sheet as retained earnings to the shareholders' equity.
Balance sheets and income statements are affected whenever a sale or cost is reported. When a company records a new sale, it increases its assets or decreases its liabilities. When a company reports expenses, it results in a decrease in assets or an increase in liabilities.
This demonstrates the close connection between the income statement and the balance sheet. While balance sheets offer a more comprehensive perspective on a business's financial stability and investment health, both documents are essential components of financial statements.
Download Now: 3 Statement Model Excel Template
Similarities Between Balance Sheet and Income Statement
The Income Statement and Balance Sheet are both components of the three Basic Financial Statements that every company must have to evaluate their strength. They share several similarities, such as:
- Accounting Method: They both utilize double-entry bookkeeping to record every business transaction, where each business should have two accounts that record either debits or credits.
- Providing Evidence: The balance sheet and income statement may give proof of the business's financial health, current performance, and continuous growth to investors or lenders to demonstrate that your company is suitable for the required loan.
- Track Business Compliance: Both statements are required to guarantee that businesses adhere to legislative guidelines.
- Financial Reporting: Both balance sheets and income statements are usually included in a company’s annual reports since they both are the key components of any financial reporting and the main indicators for a business's financial status.
- Reflect Company Performance & Activity: Both statements hold information about the financial performance and operations of a company. They focus on distinct parts of performance and give different insights, yet both statements convey information about a company's activities. The income statement reflects revenues, expenses, and net income resulting from day-to-day operations, while the balance sheet shows the assets, liabilities, and equity used to conduct those operations.
- Interconnected: The connection between the balance sheet and the income statement lies in any changes to an income statement item having an impact on the balance sheet. For example, net income from the income statement adds to retained earnings on the balance sheet, while depreciation expenses from the income statement impact the balance sheet value of property, plant, and equipment.
Although they have all the previous similarities, make sure to point out that they serve separate and different distinct purposes. The income statement is concerned with a company's profitability and performance over time, while the balance sheet is a snapshot of a company's financial health at a certain point in time. They provide a full insight into a company's financial situation if utilized together.
Read More: Main Differences Between Income Statement and Balance Sheet
Automate Balance Sheet Generation With Enerpize
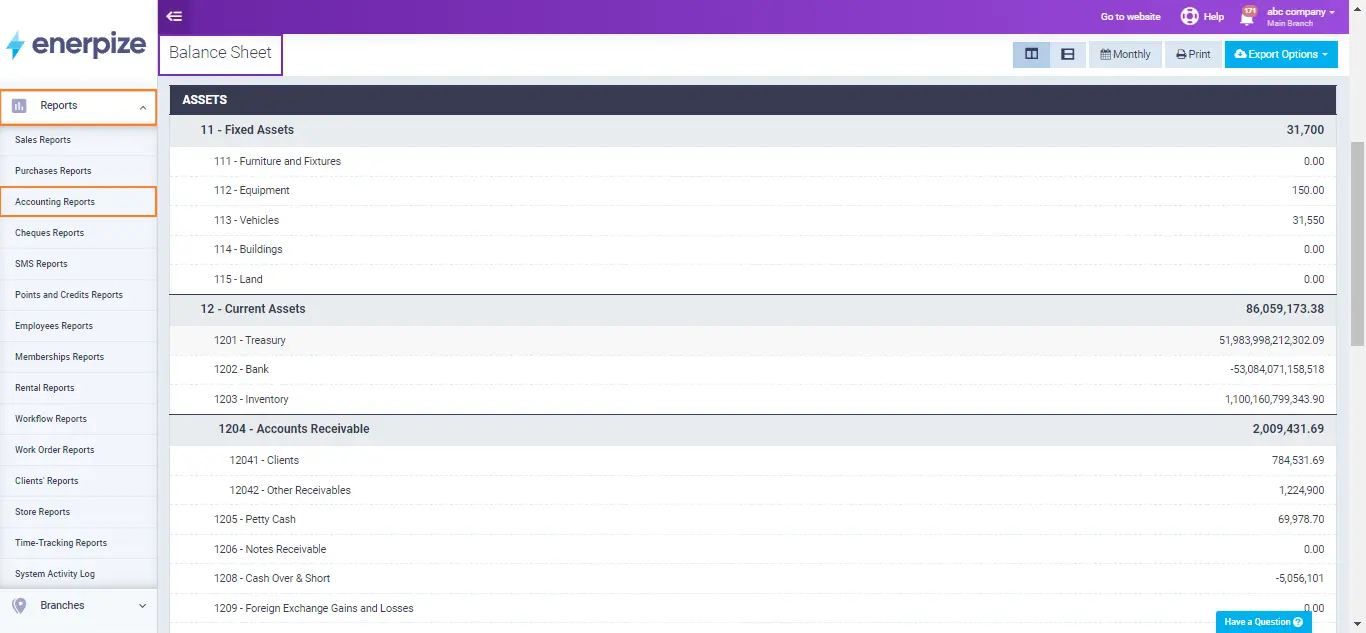
Enerpize is a comprehensive online accounting software designed to simplify financial management for businesses. With Enerpize, users can automatically create balance sheets by seamlessly tracking and recording all financial transactions. The software consolidates income, expenses, assets, and liabilities into an organized format, ensuring accurate and up-to-date financial statements. This automation not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors, providing users with a clear and reliable view of their financial health. Stay financially organized and make informed decisions effortlessly with Enerpize.
FAQs about Balance Sheets
Do Small Businesses Need a Balance Sheet?
Yes, small businesses need a balance sheet because it provides a clear overview of the company's financial situation, showing assets, liabilities, and equity. This is essential for assessing financial stability, managing liquidity, handling debt, and boosting trust with investors and lenders. It also helps in tax planning and tracking business growth over time, making it a critical tool for ensuring long-term financial stability.
Do I need a Balance Sheet for Taxes?
As a small business, you may not be required to file a balance sheet for taxes. However, if your small business operates as a corporation or partnership, or if your assets exceed specific thresholds, a balance sheet may be required. Even if it is not required, having a balance sheet helps with tax planning and proper tax filings. It can help you identify deductions and organize your finances, making tax preparation easier.
Creating balance sheet is easy with Enerpize.
Try Enerpize accounting module to create your balance sheet.








