Author : Haya Assem
Reviewed By : Enerpize Team
A Comprehensive Guide to Retail POS Systems

Table of contents:
- What is a POS system in retail?
- How to use a POS system?
- Different types of POS systems for retail
- What are the 6 components of a typical retail POS system?
- How to compare between different POS systems
- Advantages of the POS system in retail
- Disadvantages of POS systems in retail
- How Does Enerpize Contribute to Creating a Smooth POS System Experience?
- Key Takeaways
The adoption of POS systems enhanced the retail experience significantly since they have a direct impact on the efficiency and success of businesses. POS systems can streamline and expedite transactions, reducing customer wait times and allowing shops to service more customers, ultimately contributing to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
From traditional systems to cloud-based platforms and mobile solutions, the retail sector offers a myriad of POS options, each with its unique set of advantages and disadvantages. As businesses strive to align their operations with the digital age, understanding the nuances of these systems becomes paramount.
This article aims to unravel the intricacies, offering insights into various POS systems' functionalities, benefits, and potential drawbacks, and empowering retailers to make informed decisions that align with their needs and goals.
Key Takeaways
- Retail POS systems combine hardware and software to process sales, handle payments, and print receipts while linking with inventory and sales tools for smoother operations.
- They consist of components like scanners, terminals, software, and payment processors, all designed to manage sales, inventory, and customer data efficiently.
- Using a POS system effectively involves assessing needs, choosing the right setup, training staff, securing payments, and maintaining the system regularly.
- Types of POS include in-store systems, mobile POS using smartphones, cloud-based platforms for remote access, self-service kiosks, integrated systems, and open-source options.
- POS systems boost efficiency, manage inventory in real-time, track staff performance, support remote control, and integrate with online stores to enhance service.
- They help retailers speed up checkouts, reduce errors, and improve customer satisfaction by automating daily sales tasks and syncing data across channels.
What is a POS system in retail?
In retail, a Point of Sale (POS) system is a combination of hardware and software designed to facilitate and streamline transactions at the point of sale. It usually consists of a computer or terminal, a cash register, a barcode scanner, a receipt printer, and software for managing sales, inventory, and other aspects of a retail business.
The POS system calculates the total amount due by the customer, processes payment (cash, credit cards, or other payment methods), and generates a receipt.
Furthermore, it frequently connects with inventory management, sales reporting, and customer relationship management tools to offer retailers a comprehensive solution for efficient and effective operations.
How to use a POS system?
POS systems are classified into several varieties, each with its unique technique based on the needs of the business industry. However, there is a basic POS operation that is common to all POS transaction types and industries.
POS systems usually have two parts:
- Software: The main part of the POS system is the software, which plays a pivotal role in facilitating seamless transactions, inventory management, and overall business operations. It serves as the system's brain, processing sales data, tracking inventory levels, and generating real-time reports for informed decision-making.
- Hardware: POS devices include several parts that could vary based on the industry and size of the business, such as computers, tablets, or mobile devices. Other forms of POS hardware are a barcode scanner, receipt printer, cash drawer, and credit card reader.
6 Steps to effectively use a POS system
- Determine Business Needs Determine the particular needs and features required for your business type and size.
- Software: Select a POS software solution that meets your business needs and integrates well with other systems.
- Choose the Suitable Hardware: Select the appropriate POS hardware components.
- Employee Training: Train employees on how to use the POS system effectively to minimize errors and improve efficiency.
- Secure Payment Processing: Use secure payment processing to protect customer data and maintain payment industry compliance.
- Regular Maintenance and updates: Plan for regular maintenance and software updates to ensure the POS system runs smoothly and securely.
Read Also: Best Restaurant POS Systems For 2026 And How To Choose One
Different types of POS systems for retail
For retail businesses, there are various types of Point of Sale (POS) systems, each catering to various requirements and preferences. Here are the different types of POS systems that are regularly used in the retail industry:
Traditional / Instore POS systems
These are the classic, fixed-location POS systems seen at retail checkout counters. The setup usually consists of a computer, cash drawer, receipt printer, and other hardware. These systems are suitable for physical stores with set-up checkout areas.
Mobile POS systems
Smartphones serve as the primary interface for mobile POS systems. Retailers may process transactions anywhere in the store using mobile devices equipped with POS software.
This flexibility is advantageous for businesses with a more dynamic and interactive shopping experience since it allows you to handle rapid, reliable payments as well as extensive sales and inventory analytics.
Cloud-based POS systems
Cloud-based POS systems are noted for their flexibility since they provide real-time data access from anywhere with an internet connection.
These systems have several benefits, including improved adaptability and accessibility, seamless scalability, data-driven insights, and robust security. As a result, they are ideal for businesses with different locations or those seeking flexibility.
Self-service kiosk
Self-service kiosks are meant to allow customers to scan and pay for things without the assistance of a cashier. These kiosks are commonly utilized in grocery stores, supermarkets, and other large retail stores to assist in shortening queues for checkout and enhance the overall shopping experience. It usually consists of a stand with a touchscreen and a credit card reader.
Integrated POS Systems
Integrated POS systems communicate with various business management tools such as inventory management, accounting, and customer relationship management (CRM) software. This integration simplifies operations and gives an extensive overview of the company.
Open-source POS systems
Some POS systems are tailored to specific retail businesses, such as clothing, electronics, or food and beverage. These systems might include industry-specific features and functions customized to the sector's specific requirements.
What are the 6 components of a typical retail POS system?
.png)
1- Hardware
Includes computers, tablets, or mobile devices.
Barcode scanners for scanning product barcodes.
Receipt printers for printing receipts.
Cash drawers for storing cash during transactions.
Credit card readers for processing credit card payments.
Touch screen monitors for displaying information and inputting data.
2- Software
The software acts as the control center for several vital operations and serves as the core of the retail POS system. It has a user-friendly interface that allows for smooth swift transactions, as well as the ability to manage and analyze inventories and generate reports.
3- Barcode Scanning System
For scanning product barcodes, a combination of hardware (barcode scanner) and software is used. This system helps in efficient and precise product identification, inventory management, and a faster checkout process. All of these aspects help to enhance the customer experience.
4- Point of Sale Terminal
This is a physical location where sales transactions take place. It incorporates all the previously mentioned hardware components.
5- Payment processing system
A payment processing system is essential in the retail POS environment, providing customers with secure, convenient, and efficient payment options such as credit card and electronic payments while ensuring industry compliance and facilitating seamless integration with overall business operations.
Read Also: How Can Enerpize Boost Your Business As Payment Management Software?
6- Back-office system
The back-office system is an essential component in a retail POS environment, providing centralized control over various aspects of the business, allowing for data-driven decision-making, and ensuring seamless integration with other business management systems such as inventory management, employee tracking, and reporting.
How to compare between different POS systems
All POS systems are advantageous because they allow business owners to manage inventory swiftly and efficiently, assure more rapid transactions, analyze inventory, and generate reports; however, not all POS systems are suitable for all industries.
A POS system should be chosen based on several factors such as business size and requirements, and others, as stated in the following lines:
Identify Business Needs
Determine your exact needs, taking into account the industry, business size, and particular features required for efficient operations.
Feature Comparison
Consider transaction processing, inventory management, reporting tools, and integration possibilities. Determine which system best meets your company's requirements.
Hardware Compatibility
Check whether the POS system is compatible with your present hardware or if additional costs are required. Ensure that the system supports the hardware components essential for your business.
Security Measures
Prioritize systems with robust security features, including data encryption, secure payment processing, and user authentication, to protect sensitive customer and business information.
Cost Considerations
Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including upfront costs, monthly fees, and potential additional charges. Compare pricing models and choose a system that aligns with your budget.
Staff Training
Consider the level of customer support and training provided by each POS system vendor. Responsive support and thorough training materials can be crucial for a smooth implementation and ongoing usage.
Integration with Other Software
Assess how well each POS system integrates with other business tools, such as accounting software, inventory management, and e-commerce platforms. Seamless integration streamlines overall business processes.
Related Template: Retail Daily Sales Excel Report
Advantages of the POS system in retail
POS systems are changing the retail industry by improving efficiency, inventory management, and customer satisfaction. These solutions play a critical role in establishing a streamlined and customer-focused retail experience. Here are the POS system advantages in retail:
Strengthen Efficiency
POS systems streamline operations through streamlined transactions and automated procedures to improve efficiency by reducing checkout times and eliminating errors, resulting in faster retail procedures and a better overall customer experience.
Easy Inventory Management
Real-time inventory tracking and automatic reordering tools help you avoid stock-related concerns while providing exact control over supply networks. POS systems enable businesses to simply maintain ideal stock levels, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
Read more about an inventory management method: ABC Analysis Method
Easy Tracking of Employee Activity
Individual performance metrics and attendance monitoring features empower managers to track and improve staff efficiency. POS systems provide insights into employee actions, helping in the identification of high-performers and opportunities for workforce development.
Make Business Accessible from Anywhere
Cloud-based accessibility and multi-device compatibility allow business owners to manage operations remotely. Modern POS systems enable real-time data access, fostering flexibility for monitoring and controlling business activities from various locations and devices.
Enhance Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is improved by faster checkout times and personalized services. POS systems make shopping more convenient and satisfying by reducing wait times and tailoring suggestions based on customer purchase history.
E-commerce Integration
Integrating POS with e-commerce systems results in a unified inventory management experience. This maintains accurate stock data across online and physical channels, ensuring a smooth shopping experience for customers while increasing loyalty.
Disadvantages of POS systems in retail
While POS systems have great advantages, they are not without downsides. The drawbacks of retail POS systems include:
Initial Costs
A POS system requires a significant initial investment in hardware, software, and training. This might be a significant hardship for small businesses with limited budgets.
Technical Issues
POS systems may have technical glitches or outages, causing typical business operations to be disrupted. POS transactions may be delayed as a result, frustrating both customers and staff.
Internet dependency
Cloud-based POS systems rely on internet access. Any disruption in internet service might impair system operation, disrupting transactions and data access.
Security Concerns
POS systems retain critical customer and financial information. They may be at risk of hacking if not sufficiently secured, potentially leading to data leakage and compromising customer privacy.
Upgrades
Frequent software updates might be challenging for businesses that use POS systems. Upgrades may necessitate more staff training, and compatibility issues with current hardware or third-party connections may develop, potentially disrupting corporate operations.
How Does Enerpize Contribute to Creating a Smooth POS System Experience?
Enerpize POS software enables you to oversee sessions and work shifts efficiently. It presents product listings with names and images in a user-friendly interface, facilitates the creation of invoice items considering quantity, price, and discounts, and allows you to handle your cash box with distinct lists.
You can review a summary after each session, and the POS management system compiles comprehensive reports tracking the transactions of sold items and issued invoices across all sessions.
The Enerpize POS system addresses a prevalent limitation of cloud-based POS systems, which is reliance on internet connectivity. It empowers you to monitor your business's sales process even without an internet connection. Online access is only necessary during the login phase; subsequently, until the synchronization of invoices, you can operate offline without the need for an internet connection.
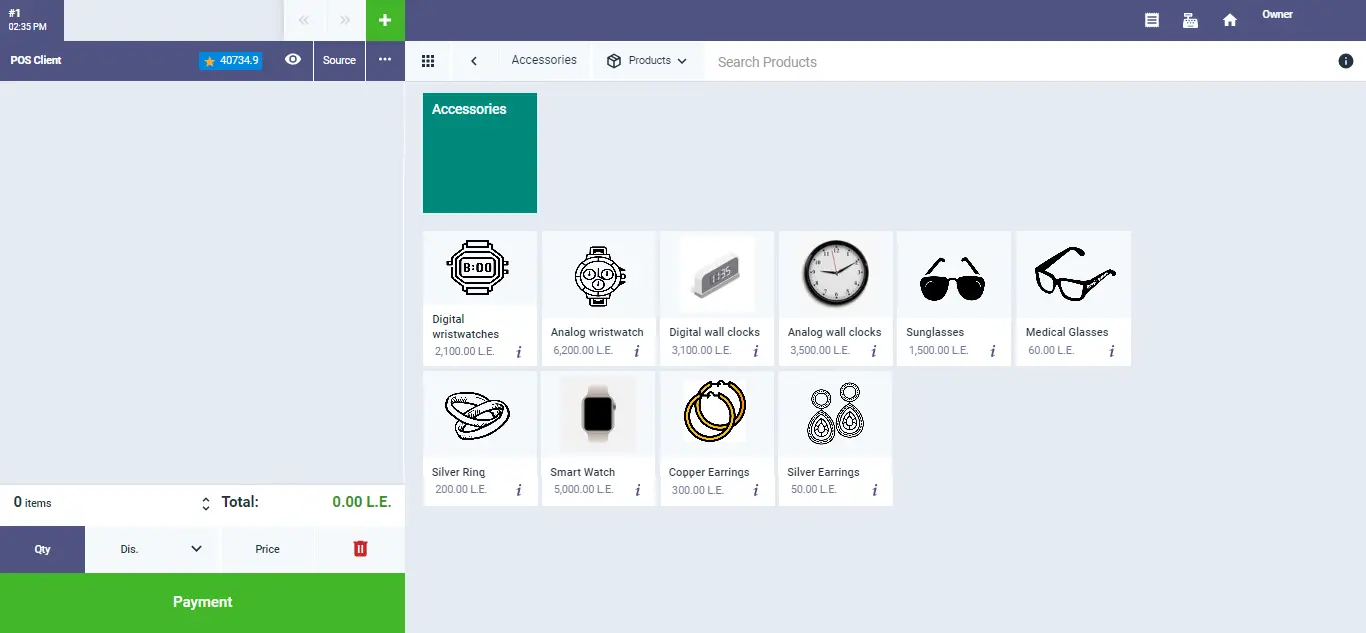
In conclusion, Enerpize POS offers efficient session management, user-friendly interfaces for products and invoices, and offline capabilities, overcoming the internet dependency common in other systems. It's a flexible and reliable solution for seamless point-of-sale operations.
Key Takeaways
A POS system in retail combines hardware and software to streamline transactions, including calculating totals, processing payments, and generating receipts. It integrates with inventory and sales tools for efficiency.
POS systems vary but generally consist of software and hardware, managing transactions and inventory. Steps for effective use include assessing business needs, selecting suitable software and hardware, training employees, ensuring secure payments, and planning regular maintenance.
Various POS systems cater to retail:
Traditional/Instore: Fixed setups for physical stores.
Mobile POS: Uses smartphones for dynamic transactions.
Loud-based POS: Enables real-time access, which is ideal for multiple locations.
Self-Service Kiosk: Quick checkout without a cashier.
Integrated POS: Communicates with management tools.
Open-Source POS: Tailored for specific retail sectors.
POS systems revolutionize retail by streamlining operations, enhancing inventory management, and boosting customer satisfaction. They facilitate efficient transactions, real-time inventory tracking, employee performance monitoring, remote business management, and seamless e-commerce integration.
Enerpize POS enhances session management with user-friendly interfaces, offline capabilities, and comprehensive reports. It overcomes internet dependency, allowing seamless point-of-sale operations and making it a flexible and reliable solution.
Retail POS Systems are easy with Enerpize.
Try our sales module to use Retail POS System