Author : Enerpize Team
The Ultimate Payroll Cheat Sheet

Table of contents:
- What is Payroll?
- How to begin with Payroll?
- How payroll is calculated?
- What is payroll processing?
- What is a Payroll Tax?
- What Payroll taxes do Employers pay and withhold from salaries?
- How much are payroll taxes Australia, United Kingdom, United States?
- How to calculate payroll tax?
- What is a payroll deduction?
- What is biweekly payroll?
- What do pay slips mean?
- How to generate payroll slips?
- How Enerpize Streamlines Payroll Management
Every business needs a payroll-organized system to use to succeed. Whatever industry you specialize in, to shine in the business world and start to make a profit, you need to know from where to start and what to give the most priority. Payroll is one of the most critical elements of any company. Otherwise, there will be severe consequences if you mess up something. So let’s start at the very beginning.
What is Payroll?
Payroll is the list of employees in your company. It can also refer to a company’s records of payments previously made to employees, including salaries or wages, bonuses, and withheld taxes, or the company’s department dealing with compensation, along with the amounts that each employee should receive for time worked or tasks performed.
All this information may be addressed in what most people call a payslip, or they use a timesheet in payroll processing to track employees’ hours and leaves. Net, gross salaries, taxes, and deductions are also included in payroll.
You could do payroll for your company by simply asking your HR to handle it. Or if you want, you can use a software or payroll service processing company to take this responsibility, similar to here there’s a module for HR with a system called Payroll Management System.
If you have a small or beginning business, you may not have yet the resources to hire a competent HR management staff to take care of this process for you.
But even if you have a big company, your best choice perhaps is payroll software. It’s easy to use, editable, almost without error in calculations, and you might want to get payroll finished without relying on people, who might get things wrong.
What puts pressure on employers while processing payroll is, it’s subject to laws and regulations in most countries. Thus, payroll must be processed correctly, otherwise, you might find yourself losing the company or even worse with a lawsuit that could lead to jail.
How to begin with Payroll?
Ok, so the first step if you decide to use payroll software is, you need to look up your country’s regulations and rules. For example, if you are in the US, then your employees need to hand you a W4 Form from the Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service. You have to make every new employee in your company supply this form for them to get paid, and to pay their taxes.
On the other hand, if you’re in the UK, then you need to register first with The HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). After you get a login, you need to set up a PAYE (pay as you earn) scheme and proceed to report your employees’ everything; their salaries or wages, deductions, and benefits.
The PAYE system is a method of paying income tax and National Insurance contributions. Employers have to deduct tax and National Insurance contributions from employees’ wages before paying them.
Of course, it goes without saying that every employee joins you, you have to notify HMRC or if there any changes with the employee’s status; if they got promoted or they go to work abroad, etc. Based on your reports, you’ll be able to view what you owe to HMRC. You’ve got to pay them, normally every month. Also, if a new employee joins you, you collect their P45 form, which declares aspects of their earnings and tax paid during the tax year.
Meanwhile, in Australia, it’s a little bit complicated process. A quick tip, If you chose to use a payroll service in reporting to the government, then you have to make sure to check if they are registered in ATO (Australian Taxation Office) or not.
However, if you are using software to calculate and manage all aspects of the report before sending it to ATO, you have to be aware of a few things. For instance, you need to make sure that they use an STP (Single Touch Payroll) solution.
There are numerous Superannuation and Pay As You Go (PAYG) laws that need to be arranged first with the ATO. To prevent penalties and fines, make sure that you use the country’s technology and specialists to ensure full compliance with payrolls.
Read more about payroll journal entries.
How payroll is calculated?
There’s no question that payroll is different for each company and business. Even in the same company, not every employee has the same payroll and calculations. However, some things are set in each payroll that you process, and all you have to do is, modify the amount itself to give you the correct result for every employee.
Initially, you have to estimate the gross pay. There are several ways to calculate that, and it depends on how you pay your employees. For example, if it’s hourly, salaried, or by a commission or a piece of work. If it’s hourly, then you set the pay rate per hour and how often do you pay them, and you’ll get their time worked calculated.
Also, you have to put into consideration the overtime hours, if there are any, to add them to their pay. For the salaried employees, it’s a little bit easier as it’s in most cases fixed, and you don’t need to go with the same process for the hourly employees. Needless to say, you, as an employer, have to ensure that what you pay your employees is met with the minimum wage your government or workforce has set.
Download Now: Free Payroll Template in Excel and Word
What is payroll processing?
Payroll Processing is the task of managing the employees’ data. It could be a complicated process but at the same time manageable. It’s a task that requires a lot of focus to not get anything wrong or miss something. Here are a few steps to guide you through the way:
1- Set Up Your Payroll Policy
By Payroll Policy, we mean the payroll that you’ve established. For example, the Pay dates, attendance and leave policy, payment methods, benefits, and such. You have to be up to date with all the regulations and laws while creating your policy.
2- Gathering Employees' Data
You have to collect all the required information from your employees to do the calculations correctly. You need to know the amount of taxes that should be deducted from each employee, their net gross pay you previously set, and benefits. And if there’s a form that has to be filled first by the worker to make sure it was completed accurately to avoid miscalculations.
If there’s health insurance or a retirement plan that your company offers, you have to get your worker’s approval that there will be further deductions.
3- Create a Timesheet for Employees
After you make sure you’ve filled in all the basic details and double-checked again, it’s time to collect how many hours each worker has spent on the pay period. Timesheets are a perfect method to make it easier for you to track hours, or if you’re using payroll software, you can organize it by automatically measuring hours, and you would only need to add the additional time.
Download Now: Free Bi-Weekly Timesheet Template
4- Calculate Payroll
If you’re using a software system, then this phase won’t take long, and it’ll be easy for you to complete it. All you have to do is insert the gross salary, taxes, and other deductions then the system will measure the net pay you have to give to your workers.
On the other hand, it could take more time if you are doing your own calculations. It’s preferable to use a spreadsheet to aid you. All you have to do is subtract the deductions from each employee from their gross salary. The money left over is the net salary, or take-home pay, of the employee.
5- Verify Payroll Reports
Once you’ve measured your payroll, you have to make sure it’s all correct. Check all the data you’ve entered, whether it’s on a system or in your spreadsheet. Be sure you’ve not miscalculated any sums or taxes because they could contribute to a legal problem in the future. Last but not least, check if there are any details you have missed.
6- Produce And Distribute Payslips
Now that you’re certain that everything is filled correctly, it’s time to fill the payslips and export them to be shared with your employees. The payslip, if you’re using payroll software, will be a click away to produce and assign. If you’re not using a software system, you can find a payslip template that suits your needs and use it.
7- Disburse Employee Salaries
You’ve already chosen the method of payment that your employees will use to collect their pay. Therefore, it’s time to deliver the payment to them. If you’re doing a Direct deposit to their bank accounts, then you have to send to the bank beforehand; the total net pay for each employee to be transferred to their account on the scheduled pay date.
There are other methods that you can use as well:
- Paper Checks
- Cash
- Mobile wallets
- Payroll Cards which is a type of prepaid card that you load your employees’ salaries onto
8- Report and update Payroll records
This step is very crucial, and you have to complete it, or otherwise, you might find a waiting lawsuit in your name. In the US, you have to keep all payroll and transaction records ready and up to date, in case your employee issues a dispute concerning their salary. Next, the IRS (Internal Revenue Service) will ask you for these reports to solve the conflict.
The UK system is different. Each month, you have to pay HMRC, the tax and national insurance you owe in the previous tax month as stated on your Full Payment Submission (FPS), minus any Employer Payment Overview (EPS) reductions you submitted, before the 19th of the current tax month.
If you have paid any staff and didn’t send an FPS or sent one late, HMRC will send you a late filing note. If you have a legitimate excuse for reporting late, they could investigate and wave it for you, otherwise, they may charge you for a penalty.

What is a Payroll Tax?
Payroll taxes are taxes placed on employers and employees. It could be categorized into two main categories, either taxes deducted from the employee’s salary or tax paid by the employer on the value of the employee’s salary.
The first tax category is when the employer has to retain a certain amount from the employee’s salary. The name differs from one country to another, in the US, it’s a withholding tax, UK calls it PAYE, and PAYG in Australia. This tax is like an advance payment to cover income tax, social security contributions, and various insurances (e.g. unemployment and disability).
The second category of the payroll tax is the one that employers have to pay. It includes Social Security taxes, Medicare taxes, Federal unemployment taxes (FUTA), and State unemployment taxes (SUTA). All will be covered thoroughly in a bit.
What Payroll taxes do Employers pay and withhold from salaries?
In most cases, employers have to pay their own taxes plus deliver the employees’ taxes to the government and federal agencies. Employers in the US have to pay:
- FUTA tax
- SUTA tax
- FICA tax
Employers have to withhold these taxes from employees salaries:
- Federal income tax
- Social Security tax
- Medicare Tax
- State and local income tax withholding
Usually, Employers use the following forms when reporting employee tax withholdings and submitting the required tax payments to the federal government:
Form 944, Employer’s Annual Federal Tax Return
Form 941, Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return
How much are payroll taxes: Australia, United Kingdom, United States?
Australia
The amount of payroll tax is based mainly on the salaries that you pay your employees. The tax rates differ from one state to another. The tax usually applies when your employees’ wages or salaries exceed a threshold that is set by your state.
These are the rates of payroll tax and the threshold for each state:
State | Annual Threshold | Tax Rate |
| Victoria | $650,000 | 4.85% |
| South Australia | $600,000 | 4.95% |
| New South Wales | $750,000 | 5.45% |
| Queensland | $1,100,000 | 4.75% |
| Australian Capital Territory | $1,750,000 | 6.85% |
| Western Australia | $750,000 | 5.50% |
| Tasmania | $1,010,023 | 6.10% |
| Northern Territory | $1,500,000 | 5.50% |
UK
There are 2 sections for Payroll Taxes:
- You, as an employer, have to pay National Insurance for all wages above £ 732.00 a month for each employee. The national insurance rate is 13.8%.
- In addition to the income tax deducted under PAYE, you must also subtract the National Insurance percentage from the salaries of your employees and pay it to the HMRC. The rates are for most employers for the 2020 to 2021 tax year according to HMRC :
| £183 to £962 a week (£792 to £4,167 a month) | 12% |
| Over £962 a week (£4,167 a month) | 2% |
US
U.S. payroll taxes could be a complex matter because there is no room for error at all. Because of certain variables that need to be calculated, for you as a business owner or when you pay for your workers. It’s a huge responsibility for you, but at the same time, it can be done with support.
1. FITW
Federal income tax withholding is an IRS-administered scheme that extracts funds based on earned income. It can be a little confusing to withhold federal income tax because you withhold a different amount from the salaries of each employee, and employees can change the amount you need to withhold.
You must deduct federal income tax and send it to the federal government from employee salaries. To fund government services such as defense, health care, housing aid, education, and veterans’ benefits, the government then uses the tax.
2. FICA Taxes
FICA stands for the Federal Insurance Contributions Act, and it includes Social Security and Medicare taxes. These taxes are required from both the employee and employer. The taxes are divided equally between them.
Its rate at the moment is 15.3% which consists of 12.4% for social security (6.2% for employer + 6.2% for employee). In addtion to Medicare, its total rate is 2.9% (1.45% employer + 1.45% employee).
There is also an added Medicare tax of 0.9% for your employees that earn over $200,000.
3. FUTA
FUTA stands for Federal Unemployment Tax Act. This a payroll tax for you as an employer that funds state workforce agencies and unemployment insurance. For each employee working for you, you’re supposed to pay unemployment tax. This not a tax that got deducted from your employees, it’s all on you.
Its rate is 6.0% for what you pay your employee in a quarter of a year. It only applied to the first 7.000$ that the employee earned. It does seem like a big sum of money to pay, especially if you’re just starting your business or you’re SMB, but don’t’ worry you don’t have to pay all that.
The reason for that is the FUTA tax credit. Every state gets an unemployment tax credit of 5.4% which will partially cover your payments. Therefore, you will end up pay only 0.6% of the taxes on the first 7.000% of what your employee earned in a quarter.
Usually, you have to use this form to report this tax withholding: Form 940, Employer’s Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return
4. SUTA
SUTA is state unemployment tax, sometimes referred to as the state payroll tax. In most states, this tax is paid by only you the employer, except in Alaska, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, the employee also contributes from their salaries. The tax applies to you once you register your business in your state and with IRS and hire your first employee.
The SUTA tax rate differs from state to state. And to calculate what you have to pay, you need to know 2 things:
a. Your state Taxable Wage Base.
b. Your SUTA rate.
Also, the SUTA tax rate may differ for a new employee you hired to an employee that worked for you for a while. The experienced employee may have a higher tax rate than the new one. This file contains SUTA rates and wage bases for 2020
5. Local tax withholdings
Employers are also responsible on behalf of workers for paying state and local (city, county, etc.) payroll taxes. As with the federal payroll tax, part of that tax is paid by the employer, and the other is paid by the employee.
Bear in mind that “Employee Paid” actually means that you the boss, deduct a certain amount from the paycheck of your employee, then pass it as part of your payroll taxes. These withholdings are based on every state and local areas’ regulations. You can check The Federation of Tax Administrators website for more details.
How to calculate payroll tax?
Payroll taxes could be complex, especially if you’re doing it yourself. If you’re using payroll software, then it should not be so complicated. You just have to make sure that you entering the correct data in the correct place. Then you export the results to fill your repost that you’ll submit to the government. Some systems even do this step for you.
On the other hand, if you decide to do your payroll taxes yourself, nothing is wrong with that, then you need to pay your undivided attention to this coming information.
If you’re doing your employees taxes, then these are the steps you need to take:
- Calculate Gross Pay: which you pay your employee without any deductions.
- Calculate Employee Tax Withholdings: You’ll need to deduct federal, state, and FICA taxes from each paycheck in most states. Which you will know from their W-4 form that mentions gross pay and the number of allowances.
- Calculate Federal Income Tax (FIT): Federal Income Tax (FIT) is determined using the completed W-4 details of the employee, their taxable compensation, and their pay frequency. You can use either the Wage Bracket Method or the Percentage Method to determine FIT, which you will find in Publication 15-T (2021).
Here’s an example of the Percentage Method below. After you adjust the employee’s wage amount, calculate the tentative withholding amount, then estimate the tax credits. - Calculate FICA Taxes: The social security tax rate is 6.2%. Hence, you’ll take your employees’ gross pay and multiply it by 6.2% and withhold the amount that appears to you. Medicare tax also goes the same way, only you multiply the gross pay by 1.45%.
- Calculate State and Local Taxes: Calculating state taxes is a similar running when you know how to measure FIT and FICA taxes. Only you need to check your state for the tax percentage as it differs from one state to another. You just need to search your state for a tax percentage that varies from one state or local area to another.
The second part is calculating your employer Payroll Taxes :
- Calculate FICA Taxes: You are expected to comply with the FICA tax withholding of the employee, which ensures that the company will pay 6.2 % Social Security tax and 1.45 % Medicare tax.
- Calculate Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA): The tax is 6.0 % of each employee’s first $7,000 in earnings each year. You will earn a federal tax rate deduction of up to 5.4 % if the company is subject to state unemployment, which makes the effective tax rate of 0.6 %.
- Calculate State Unemployment Tax (SUTA): The Unemployment Tax (SUTA) rate varies by region. Consult the Department of Labor or Unemployment Revenue of your state for tax rates, pay bases, and filing requirements.

What is a payroll deduction?
There are certain deductions that like we said as an employer, you have to withhold from your employees’ pay before they receive it. These deductions vary some are voluntary and some are obligatory.
- Obligatory Payroll Tax Deductions:
- FUTA tax withholding
- FICA taxes
- State income tax withholding
- Local tax withholdings
- Court-ordered payments for child care
- Voluntary Payroll Deductions:
- Retirement plans
- Health insurance premiums for medical, dental, and vision plans
- Life insurance premiums
- Contributions to a flexible spending account or pre-tax health savings plan
- Short term disability plans
- Job-related expenses (eg. Uniform and/or tools)
- Tuition and /or Certification deductions
- Donations for interoffice charity
What is biweekly payroll?
Most people are familiar with the monthly payroll system and it’s the most used in companies. But there is another way you can process your employees’ payroll. It’s always good to see the available options and then decide if it will work for you best.
It means when you pay your employees every 2 weeks. This means they will be paid 26 times per year, usually twice a month. It could be also 3 times in month depends on the payday you specified.
Pros:
- Your employees will get paid regularly which will motivate them more.
- They will feel like it’s easier for them to manage their budget and spending.
Cons:
- It will take more accounting effort to process the payroll.
- It will be harder to divide the taxes and to calculate them every 2 weeks.
What do pay slips mean?
Payslip is simply a document you issue for your employees that explains their salaries or wages. This document details the gross pay, taxes, and deductions, and net pay. In some countries like the US, you’re obligated to issue a payslip for your employee every time you pay them.
In the US, the payslip includes, of course beside the above information:
- Gross Taxable Pay
- Tax Deductions
- Pay Period Dates
- Method of Payment (whether it’s via check or bank transfer)
- Hours Worked
In the UK, the payslip includes:
- National Insurance (NI) number
- Payroll number
- Tax Code
- Method of cashing the payment
- Bonuses and overtime worked
- Tax Period
How to generate payroll slips?
If you’re using payroll software, it should be easy to fill in the payslip and extract it. It also saves you a lot of time if you have a set template on this program that you use for all your employees and all you have to do is change the data of each employee. You may also easily go to Microsoft Office and search all the options they provide to payslips or spreadsheets and download them.
Of course, each organization and corporation will have its own specifications, so it is preferable to subscribe to a software that fits your needs. And if you haven’t found anything suitable, some things are set in any payslip you meet, and all you have to do is change them or add blocks to your choice.
Download Now: free payslip template from Enerpize.
How Enerpize Streamlines Payroll Management
Enerpize simplifies payroll management by allowing you to extract payslips for all employees with one click, including basic salary components, benefits, and deductions based on attendance and leave records. Customize salary structures according to job roles, departments, and employment levels, and apply specific templates within employee contracts.
Our payroll management system creates custom earnings and deduction rules using variables such as attendance days, delays, and overtime hours. Easily issue payslips for groups or individual employees, integrating attendance records for accurate payroll calculations. View comprehensive reports on total salaries paid, filtered by organizational structure, departments, or individual employees, for different pay periods, and track net salaries monthly or annually.
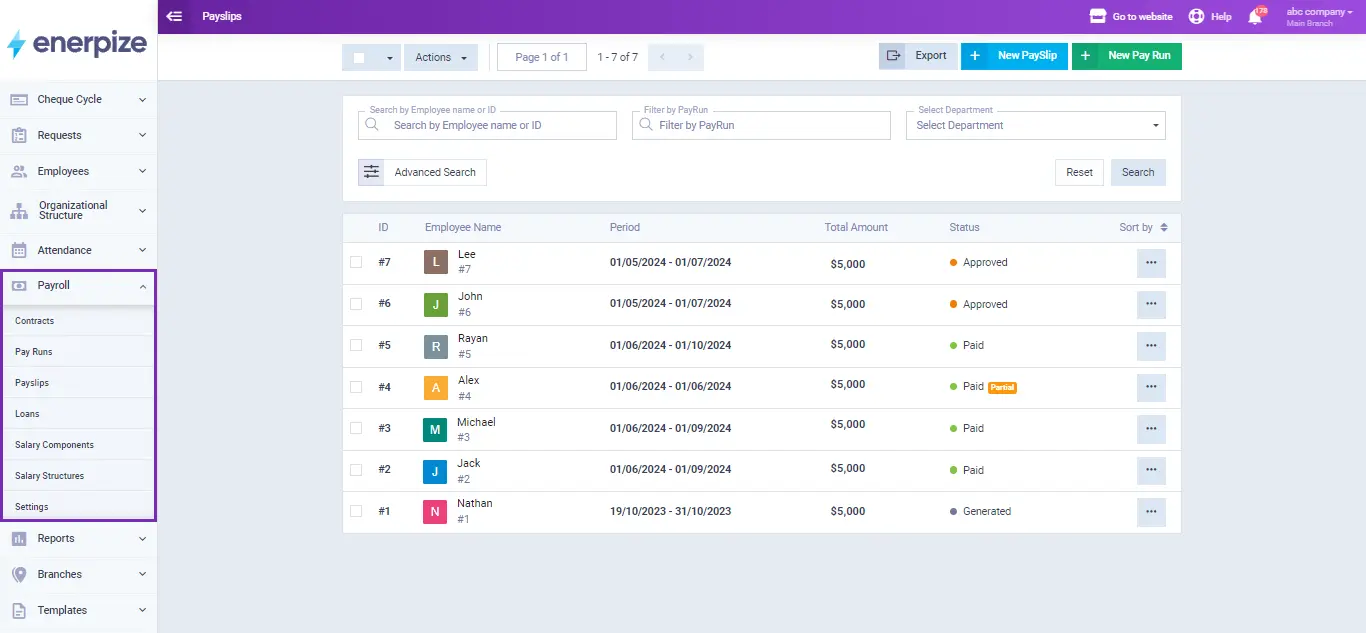
Payroll calculation is easy with Enerpize.
Try the Enerpize payroll module to calculate your employees' payroll





