Author : Enerpize Team
What Is an Invoice and What Does it Look Like? A Complete Guide

Table of contents:
Issuing an invoice is an integral part of business communications; whether you want to charge a customer for purchased products or bill clients for rendered services, an invoice is not only a document that facilitates payment but, more importantly, a business document that provides legal protection.
In this guide, we aim to take a deeper dive into invoicing. We will define an invoice, outline the different types, explain how to create one, provide templates, and answer the most common questions about invoicing for businesses and freelancers.
Key Takeaways
- An invoice is a legal and financial document issued before payment to record a business transaction and request payment from a client.
- Invoices should not be confused with receipts, which are issued only after payment is completed.
- Different types of invoices—such as sales, VAT, recurring, commercial, and digital—serve specific business, accounting, and regulatory needs.
- Accurate invoicing is essential for accounting, tax compliance, payment tracking, and legal protection.
- A professional invoice includes seller and buyer details, a unique invoice number, itemized charges, taxes, payment terms, and due dates.
- Invoice numbers help with record-keeping, fraud prevention, payment accuracy, and audit readiness.
- Invoicing software automates invoice creation, tracking, reminders, and reporting, reducing errors and saving time.
- Cloud-based invoicing solutions like Enerpize help businesses get paid faster and manage invoicing efficiently from anywhere.
What Is an Invoice?
An invoice is a financial document issued by a seller or service provider to a buyer or client that records a business transaction and states the amount due for payment. It lists all products or services a client owes to a business, with a record of all costs under a specific agreement.
An invoice enables businesses to issue and collect payments from their clients. It helps reserve the seller's or service provider's right to the purchased products or services owed. In addition, it is vital to maintain records of business transactions.
Functions of an invoice
- An invoice helps businesses track products and services provided, the total amount due, and customer records.
- It serves as a legal record, including payment statement documentation and the agreement of payment terms and conditions in the invoice.
- An invoice is an indispensable tool for accounting. It helps track payments due, taxes, sales performance and streamlines the business's books.
Common Types of Invoices
Invoices are more than simple billing documents—they play a vital role in documenting transactions, defining payment terms, and ensuring financial and regulatory accuracy. Businesses rely on different types of invoices based on the nature of the transaction, industry requirements, and whether payments are recurring, tax-related, or linked to purchase orders.
Using the appropriate invoice type helps organizations maintain clear records, improve cash flow management, reduce disputes, and support efficient financial tracking and analysis. In the following section, we will explore the different types of invoices and the purpose of each one:
1- Sales & Payment Invoices
These invoices are used for standard sales transactions and payment collection.
Proforma Invoice
A pro forma invoice is a preliminary invoice issued before goods or services are delivered. It is used to inform buyers of expected costs and terms, but is not legally binding. It includes seller and buyer information, product or service descriptions, estimated quantities, prices, and delivery and payment terms.
You can download the Proforma Invoice Template
Sales Invoice
A sales invoice is issued by a seller to request payment for goods or services delivered. It is used to record revenue and start accounts receivable. The sales invoice includes seller and buyer information, product or service details, quantities, unit prices, taxes, total amount, and payment terms.
You can download the Sales Invoice Template Excel
Issuing sales invoices with Enerpize is impressively simple: select or quickly add your client, choose items, enter prices and tax rates, and let the system calculate the total. Then, your invoice is ready to be saved or sent immediately.
Watch the video below to learn how to create sales invoices using the Enerpize system:
Credit Invoice (Credit Memo)
A Credit invoice is issued to reduce the buyer's outstanding balance resulting from returns, overbilling, or service adjustments. It is used to maintain accurate financial records. The contents include the original invoice reference, the amount credited, the reason for credit, and the updated balance.
Debit Invoice (Debit Memo)
A Debit Note increases the amount owed by the buyer, typically for additional charges or corrections. It ensures accurate accounting. Contents include seller and buyer details, original invoice reference, additional charges, reason, and updated balance.
Commercial Invoice
A commercial invoice is used for international trade to request payment and for customs clearance. It includes seller and buyer details, product descriptions, quantities, weight, shipment details, customs and tax duties, terms and conditions, and total value.
You can download the Commercial Invoice Template
Overdue Invoice
An overdue invoice is sent when payment is not received by the due date. It serves as an official reminder and may include late fees or updated payment instructions.
Consolidated Invoice
A consolidated invoice combines multiple invoices into a single document, simplifying billing, reducing administrative work, and improving payment efficiency.
Retainer Invoice
A retainer invoice requests an upfront payment for ongoing services. It is commonly used by consultants and agencies to ensure steady cash flow and long-term engagement.
Mixed Invoice
A mixed invoice includes both credit and debit adjustments, showing the net balance in a single document for easier reconciliation.
Final Invoice
The final invoice is issued after project completion to request remaining payments. It summarizes the total project cost. Contents include seller and buyer details, project description, total cost, payments received, remaining balance, and payment instructions.
2- Project-Based Invoices
These invoices are essential for taxation, auditing, and legal compliance.
Timesheet Invoice
Timesheet Invoice charges clients based on hours worked. It is used in professional services or contract work. Contents include seller and buyer details, hourly rates, total hours worked, task descriptions, subtotal, and total payment due.
Recurring Invoice
A recurring invoice is automatically generated at regular intervals for subscriptions or ongoing contracts. It ensures consistent cash flow and simplifies repeat billing. It contains seller and buyer details, recurring item descriptions, quantities, prices, payment terms, billing frequency, and due dates.
Interim Invoice
An interim (Progress) Invoice is issued during a project to cover partial work completed. It ensures steady cash flow. The invoice contains seller and buyer information, project milestones, percentages of completion, itemized charges for completed work, and payment terms.
3- Digital & Automated Invoices
These invoices are created and managed electronically using invoicing software.
Digital Invoice
A digital invoice is an electronically created invoice, typically in PDF, Word, or Excel format. It replaces paper invoices for faster delivery and easier archiving. Contents include seller and buyer details, item descriptions, quantities, prices, total amount, and payment instructions.
E-Invoice (Electronic Invoice)
E-Invoice is a structured digital invoice transmitted directly between systems for automated processing and regulatory compliance. It is used to improve efficiency and accuracy. It contains seller and buyer information, invoice number, date, line items, taxes, total amount, and compliance codes.
4- Other types
VAT Invoice
A VAT Invoice is issued by businesses when goods or services are sold for VAT purposes. It is used for tax reporting and allows buyers to reclaim VAT. The invoice includes the supplier’s VAT registration number, the VAT rate, total VAT charged, buyer and seller details, item descriptions, quantities, and prices.
You can download the VAT Invoice Template
Expense Report Invoice
An expense report invoice is used to reimburse employees or contractors for business-related expenses, supported by receipts and approval processes.
PO Invoice (Purchase Order Invoice)
A PO Invoice is created in response to a buyer’s purchase order and ensures that the invoice matches the agreed quantities, prices, and terms. It is primarily used for automated approvals and faster payments. Contents include the PO number, seller and buyer information, itemized goods or services, quantities, unit prices, and total amount.
Non-PO Invoice
A non-PO invoice is issued when no purchase order exists, typically for ad hoc purchases or services. It is used for one-off transactions and requires manual review. The invoice includes the seller and buyer details, a description of goods or services, quantities, rates, the total amount, and the payment terms.
B2B Invoice
A B2B Invoice is issued between two businesses and usually includes detailed line items, tax information, payment terms, and references to contracts or purchase orders. It is used for compliance, audit purposes, and business transactions. It contains seller and buyer details, product or service descriptions, quantities, unit prices, taxes, and total amount due.
Choosing the right invoice type helps streamline payment management, maintain financial accuracy, and enhance professionalism with clients. Whether it’s a tax, recurring, or commercial invoice, using the appropriate type ensures faster, more organized, and error-free billing.
What Does an Invoice Look Like?
An invoice should be simple and concise, readable, and professional. It should specify all the proper information a client exactly needs to complete their payment.
An invoice should include:
- Your business ID, name, logo, and contact details
- Your client’s name and contact details
- The word “Invoice”
- Invoice ID or number
- A list of all products purchased or services rendered
- Total payment amount due
- Applicable taxes
- Payment terms and conditions
- Payment due date
- Invoice issuing date
This is a sample of how an invoice should look like:
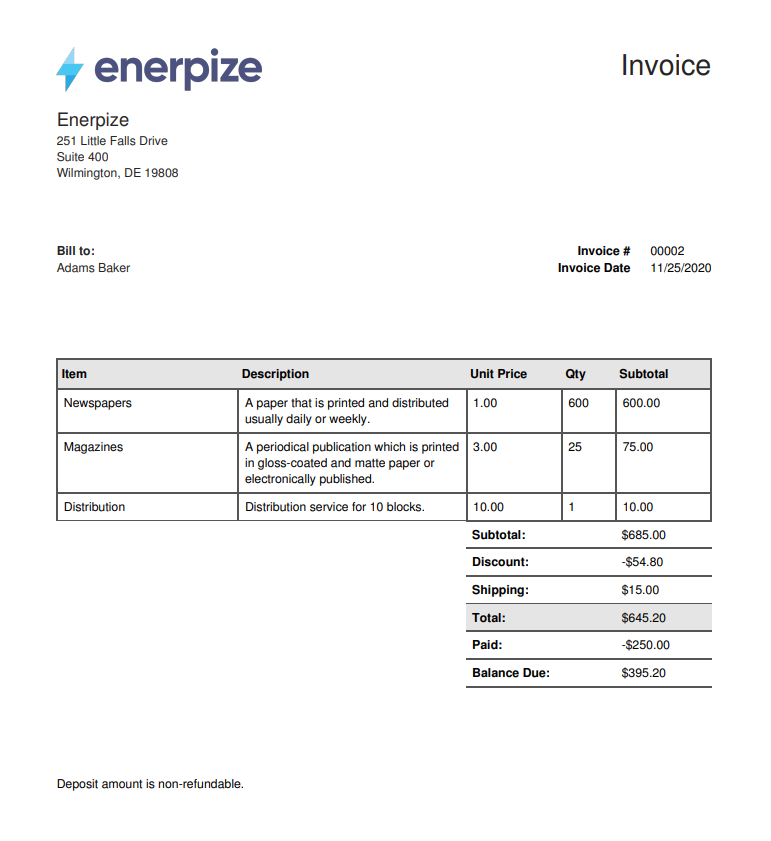
Screenshot from an enerpize software sample invoice
What Is an Invoice Number?
An invoice number is a unique identifier assigned to each invoice a business issues. It serves as a reference point for tracking transactions, organizing records, and maintaining accurate accounting. Invoice numbers also act as legal documentation, verifying the goods or services provided and the amount owed.
Benefits of Using Invoice Numbers
- Organized Record-Keeping: Invoice numbers help businesses easily locate, review, and track invoices.
- Accurate Payment Processing: Customers reference invoice numbers to ensure payments are applied correctly.
- Legal and Tax Compliance: Unique invoice numbers simplify audits, tax reporting, and financial recordkeeping.
- Improved Customer Service: In the event of disputes or queries, businesses can quickly locate the relevant invoice.
- Fraud Prevention: Sequential, unique numbering prevents duplicate and fraudulent invoices.
How to Create an Invoice Number
- Sequential Numbering: Assign numbers in order (e.g., 001, 002, 003).
- Date-Based Numbering: Include the date in the invoice number (e.g., 260114-001 for January 14, 2026).
- Customer or Project Codes: Add customer or project identifiers for easier tracking (e.g., ABC-001).
- Hybrid Methods: Combine sequential numbers, dates, and codes for a unique system.
- Automation: Use accounting software to automatically generate unique invoice numbers and prevent duplicates.
How To Create an Invoice?
Creating an invoice is an essential step for any business, freelancer, or service provider. A well-crafted invoice not only helps ensure timely payment but also supports professionalism, clear communication, and accurate financial records. Here’s a complete guide on how to create an invoice efficiently and effectively.
Required Information for an Invoice
Before you start, make sure to gather all the necessary details to include in your invoice:
- Seller’s Information: Include your business name, address, contact details, and tax identifiers such as VAT number or business registration ID. For sole proprietors, include your name and contact information.
- Buyer’s Information: Include your client’s name, business name (if applicable), address, and contact details. In some regions, like Australia, invoices for sales above a certain amount must also include the buyer’s tax number.
- Invoice Number: Each invoice should have a unique identifier, such as a sequential number, date-based, customer-specific, or a combination of these.
- Dates: Include the invoice date, supply or service date, and payment due date.
- Products or Services: Provide a detailed, itemized description of goods or services, including quantities, unit prices, and line totals.
- Costs and Subtotal: Clearly outline individual item costs and subtotal before taxes or discounts.
- Taxes: Include applicable taxes, such as VAT or GST, specifying the type and rate.
- Discounts and Additional Charges: Apply any discounts, shipping, or other fees as needed.
- Total Amount: Show the final amount due after adjustments.
- Payment Terms: Specify acceptable payment methods, due dates, and any late payment penalties.
- Notes (Optional): Include additional comments, instructions, or a thank-you message to your client.
Choosing the Right Invoice Format
You have several options for creating an invoice:
- Word Processor or Spreadsheet: Good for small businesses or one-time invoices.
- Invoice Templates: Pre-designed templates ensure consistent branding and professionalism.
- Invoicing Software: Ideal for businesses with recurring invoices, progress billing, or large projects. Software can automate numbering, reminders, and record-keeping, reducing errors and saving time.
Best Practices for Creating an Invoice
- Use a Professional Layout: Your invoice should be easy to read, branded with your logo and colors, and reflect professionalism.
- Itemize Products or Services: Detail each product or service to avoid confusion and disputes.
- Clarify Payment Terms: Clearly state the due date, accepted payment methods, currency, and late payment penalties.
- Send Invoices Promptly: Timely invoices improve cash flow and ensure quicker payments.
- Follow Up on Payments: Use polite reminders for overdue invoices to maintain professionalism.
- Keep Accurate Records: Maintain organized copies of all invoices for financial management, audits, and tax purposes.
- Leverage Technology: Digital invoicing platforms can automate recurring invoices, payment reminders, and record-keeping.
- Add Personal Touches: Include personalized notes or gratitude messages to strengthen client relationships.
- Make Payments Easy: Offer multiple payment options and, where possible, include direct payment links in the invoice for faster processing.
By following these steps and best practices, businesses can create professional, accurate invoices that improve cash flow, reduce payment delays, and enhance client trust. Whether you’re sending a one-time invoice, recurring billing, or progress payments for larger projects, clear and structured invoices are the backbone of efficient financial operations.
Free Invoice Templates
Free invoice templates are an easy and efficient way for businesses, freelancers, and service providers to create professional invoices without starting from scratch. They come pre-formatted with essential sections like business and client details, itemized charges, taxes, and payment terms, helping you save time, reduce errors, and maintain consistency across all your invoices.
You can download a free invoice template to get started immediately.
Why are Invoices Important for Business?
An invoice is a fundamental business document used to formally record sales transactions and request payment from customers. While their primary function is to support revenue collection, invoices also serve several additional purposes essential to financial accuracy, legal protection, and business efficiency for both sellers and buyers. Here are the Key Purposes of an Invoice:
1- Accounting and Bookkeeping
Invoices provide a reliable record of all sales transactions, making them essential for bookkeeping and financial reporting. They help businesses track income, measure profitability, and accurately monitor cash flow.
2- Tax Records and Compliance
Invoices serve as official documentation to support tax filings and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Maintaining organized invoices helps businesses report income and expenses correctly and prepare for audits or tax reviews.
You can download the Tax Invoice Template
3- Legal Protection
An invoice acts as legal proof of a transaction, outlining the goods or services provided, agreed-upon prices, and payment terms. This documentation helps protect both buyers and sellers in case of disputes, claims, or legal challenges.
4- Payment Tracking
Invoices help businesses and customers track payments made and outstanding balances. They simplify accounts receivable management and ensure timely follow-ups on unpaid amounts.
5- Inventory Management
For businesses dealing in physical goods, invoices help monitor inventory levels. Sales data from invoices helps forecast demand, plan restocking, and prevent overstocking or shortages.
6- Business Analysis and Planning
Invoice data can be analyzed to identify purchasing patterns, peak sales periods, and customer behavior. These insights support informed decision-making and more effective marketing strategies.
7- Record-Keeping for Buyers
For buyers, invoices serve as official purchase records, supporting expense tracking, financial reporting, warranty claims, and tax deductions where applicable.
An invoice is more than a payment request—it is a critical document that supports financial accuracy, legal protection, and efficient business operations. Proper invoicing helps businesses maintain transparency, ensure compliance, improve cash flow, and build professional relationships with customers.
You may also like: Invoice Management: Definition, Process, and How It Works
How To Send an Invoice?
Sending an invoice is a critical part of managing your business finances and ensuring a healthy cash flow. A well-organized invoicing process helps you get paid faster, reduces delays, and strengthens your professional relationship with clients.
Below is a streamlined, step-by-step guide to sending an invoice effectively:
1- Understand Your Client’s Invoicing Requirements
Before creating an invoice, take time to understand your client’s billing process. Some clients may require specific details, such as a purchase order number, a specific invoice format, or submission via a designated system. Knowing these requirements in advance helps prevent rejections or processing delays.
2- Set Up Your Invoicing System
Decide how you want to create and send invoices. You can use a simple invoice template, a word processor, a spreadsheet, or dedicated invoicing or accounting software. Automated tools can save time, reduce errors, and simplify tracking and follow-ups.
3- Prepare the Invoice
Create the invoice using your chosen system or template. Make sure it includes all essential information:
- Your business name and contact details
- Client name and address
- A unique invoice number
- Invoice and service dates
- An itemized list of products or services
- Subtotal, taxes, fees, and total amount due
- Payment terms and due date
Review the invoice carefully to ensure all details and calculations are accurate.
4- Choose the Delivery Method and Send the Invoice
Invoices are most commonly sent via email as a PDF attachment, allowing clients to download, print, or store the document easily. Include a brief, professional message in the email body referencing the invoice. If you’re using invoicing software, you can send the invoice directly through the platform to the client’s registered email.
5- Track the Invoice
After sending the invoice, monitor its status. Keep track of the due date and confirm receipt of the invoice. Many invoicing tools allow you to set reminders or notifications for unpaid invoices.
6- Follow Up on Payment
If payment is not received by the due date, send a polite reminder or follow up with the client to check for any issues. Clear communication and timely follow-ups often resolve delays without conflict.
7- Record Payment and Maintain Records
Once payment is received, record it in your accounting system and issue a receipt or payment confirmation if required. Store copies of invoices, receipts, and related communications securely for tax reporting, audits, and future reference.
A clear and consistent invoicing process not only helps you get paid on time but also improves financial organization and client trust. Whether you use templates or invoicing software, following these steps ensures smoother billing, better cash flow management, and more professional business operations.
Enerpize invoicing software is integrated with our sales and CRM modules, where you can have your list of registered clients, issue invoices without duplicates or re-entering clients’ data, and get paid in no time.
How To Pay an Invoice?
Once an invoice is received, choosing the right payment method is the next critical step. Sellers usually specify accepted payment methods and terms directly on the invoice, but businesses should still consider factors such as security, speed, fees, and ease of reconciliation before making a payment.
Below are the most common and safest invoice payment methods used today, along with their key advantages and limitations:
1- Bank Transfers and Direct Deposits
Bank transfers are one of the most reliable ways to pay invoices, especially for business-to-business transactions and high-value payments. Domestic systems such as ACH in the U.S. and SEPA in Europe enable low-cost transfers directly between bank accounts.
However, international bank and wire transfers can be slower and more expensive due to currency conversion fees and additional requirements such as SWIFT, IBAN, or BIC codes. Accuracy is critical, as errors can be difficult to reverse.
2- Credit and Debit Cards
Paying invoices by credit or debit card is fast and convenient, particularly for online and digital invoices. Card payments often include added security features and, in some cases, rewards or cashback.
However, processing fees—typically 1%-3%—can make this method costly for vendors, especially for large transactions. As a result, some businesses restrict card payments or delay payouts until processing is complete.
3- Digital Payment Platforms
Third-party payment platforms such as PayPal, Stripe, Square, and similar services simplify invoice payments by combining invoicing, payment processing, and record tracking in one system.
These platforms support multiple payment options and are especially useful for cross-border transactions. The trade-off is higher transaction and foreign exchange fees, which can significantly increase costs over time.
Explore more on this topic: 7 Ways to Accept Payments Online
4- Digital Wallets
Digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay are designed for speed and simplicity. They allow users to pay invoices quickly using stored payment details and are often integrated with mobile devices. While ideal for fast payments and international use, digital wallets are not yet universally accepted for all B2B transactions.
5- Automatic and Recurring Payments
Automated payments are commonly used for recurring invoices or subscription-based services. Once both parties agree on the amount and frequency, payments are processed automatically via direct debit or recurring card charges.
This method reduces administrative work, prevents missed payments, and improves cash flow predictability. Payment confirmations or receipts should be issued after each transaction.
6- Cash and Checks
Cash and checks are among the oldest invoice payment methods, but their use has declined significantly. While they may still be suitable for small, local transactions, they carry risks such as loss, theft, forgery, and delayed processing. Additionally, manual recordkeeping makes them inefficient and difficult to scale for modern businesses.
Each invoice payment method has its own strengths and trade-offs. The safest and most efficient option depends on transaction size, location, urgency, and cost considerations. By offering and choosing secure, modern payment methods, businesses can reduce payment delays, lower risk, and improve overall financial efficiency.
Streamline Invoicing with Enerpize
Enerpize Invoicing and Billing Software can streamline your invoicing process, from creating and sending invoices to following up on payments and generating detailed reports.
The benefits are numerous: whether you’re a freelancer or a small business owner, adopting invoicing software will provide your business with an all-in-one, reliable, integrated solution that runs smoothly.
Below are the key benefits of using Enerpize invoicing software:
Automated, customizable invoicing
Invoicing software handles your invoices; you never have to re-enter your data when issuing an invoice. You can use a pre-saved template and customize it to include the necessary information. This strengthens your business’s brand by creating consistency and credibility.
In addition, you can automate your workflow with recurring invoices, reminders, and follow-up emails to clients to ensure consistent communication and on-time payments.
Multiple Payment Gateways for Faster Payments
Good invoicing software offers multiple online and offline payment options to streamline client payments. It also offers the option of automating your payments.
Record keeping
With invoicing software, you keep all your records and invoices in one secure place, without having to worry about paper trails or invoice numbering. You can track and review any invoice at any time, from any device.
Operations integration for freelancers
Integrated invoicing software allows you to track time on projects, assign billable hours to invoices, and invoice clients for the time spent on the service rendered.
Inventory integration
Whether you’re a seller or service provider, an all-in-one invoicing system is integrated with sales and inventory management modules, which makes the process of creating an invoice expeditious. Your products or services can be saved with their price or an hourly rate per service, making it easier to maintain your records and data entry.
CRM Integration for Better Client Relationships
As a freelancer or business owner, your biggest goal is to maintain and retain clients, and it’s a no-brainer how CRM integration in an invoicing software supports such an objective.
Using it, you maintain better client relationships by keeping client information and records. It helps you personalize communication, track your clients’ business transactions and payments, and follow up with them professionally.
Choose your industry and register with our free plan to access all our modules and elevate your invoicing to the next level.
FAQs
Does an invoice mean it’s paid?
No, an invoice does not mean it has been paid. It is a legal record and a payment request that outlines the cost of products or services and the total amount due.
It is issued before payment to inform clients of the payment details, terms and conditions, and the due date. Proof of payment is provided through a sales receipt, not an invoice.
What are the differences between invoices, bills, and receipts?
An invoice is a legal and financial document issued before payment. It records a business transaction and formally requests payment from a client, detailing the products or services provided, prices, taxes, payment terms, and the due date. An invoice remains unpaid until the amount due is settled.
A bill refers to the amount owed for goods or services and represents the obligation to pay. An invoice is the formal, documented version of a bill, clearly outlining what is owed and the terms under which it is owed.
A receipt is issued after payment is made. It serves as proof of payment and confirms that the amount listed on the invoice or bill has been paid, in whole or in part. Receipts are used for record-keeping, accounting, and verification purposes.
Is an invoice a proof of purchase?
No, an invoice is not a proof of purchase. It is a legal and financial document issued before payment to request payment for goods or services provided. Proof of purchase is provided after payment, usually in the form of a receipt.
When should I send an invoice?
You should send an invoice after delivering goods or services, or according to the agreed-upon terms, such as upfront for retainer payments or partially during a project (interim invoice). Timely invoicing improves cash flow and ensures faster payments.
When would you use an invoice?
You would use an invoice to:
- Request payment from a client for goods or services delivered.
- Track sales and accounts receivable.
- Maintain legal and financial records.
- Document taxes, VAT, or other regulatory requirements.
- Bill for recurring services or subscriptions.
Essentially, invoices are used whenever you need to formally request payment and document a transaction.
Can you pay without an invoice?
Yes, payment can occur without an invoice, but it is not recommended. Without an invoice, there’s no formal record of what is being paid, which can create accounting, tax, and legal issues. Invoices provide clarity, proof of transaction, and proper record-keeping for both parties.
What is the main purpose of an invoice?
The main purpose of an invoice is to formally request payment for goods or services provided while also serving as a legal, financial, and accounting record of the transaction. Invoices support payment tracking, tax compliance, legal protection, and overall business organization.
Invoicing is easy with Enerpize.
Try our sales module to issue software invoices easily





