Author : Madonna Adel
What Is Accounts Receivable (AR)? And How To Improve?

Table of contents:
- Key Takeaways
- What Is Accounts Receivable?
- What Is Accounts Receivable accounting?
- Accounts Receivable Examples
- Is Accounts Receivable an Asset?
- Accounts Payable VS Accounts Receivable
- Importance of Accounts Receivable for Business
- How to Calculate Accounts Receivable?
- How to Reconcile Accounts Receivable?
- How do You Record Accounts Receivable?
- What is the Accounts Receivable Process?
- How to Manage Accounts Receivable Effectively?
- What is Accounts Receivable Financing?
- How Enerpize Streamlines Accounts Receivable Management?
- FAQs
Customers owe you. Managing invoices, monitoring incoming payments, and keeping an eye on outstanding balances – all of this is part of handling accounts receivable. But accounts receivable is more than just tracking money; it plays a key role in cash flow, financial planning, and the overall health of your business.
In this article, you will learn what accounts receivable are, why they are considered assets, and how businesses can manage them effectively. We will also explore the accounts receivable process, common challenges, and practical tips for improving collection and maintaining a healthy cash flow.
Key Takeaways
- AR represents money a business is owed by its customers for goods or services delivered but not yet paid for. It is considered a current asset on the balance sheet.
- When a sale is made on credit, AR is recorded as a debit, and revenue is credited. Payments received reduce AR and increase cash or bank balances.
- AR shows money owed to your business (asset), while accounts payable shows money your business owes to suppliers (liability).
- Proper AR management supports cash flow, working capital, and accurate financial reporting.
- Metrics like Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), Accounts Receivable Turnover, and Cash Conversion Cycle help monitor and improve collection efficiency.
- Use digital invoicing, track KPIs, standardize billing, automate reminders, and set clear credit policies to maintain healthy receivables.
- AR can be used as collateral for financing to free up cash and support day-to-day operations.
- Regular reconciliation ensures AR balances are accurate, reduces errors, and improves cash flow control.
What Is Accounts Receivable?
Accounts Receivable (AR) is the money a business is owed by its customers for goods or services that have been delivered but not yet paid for. Essentially, it reflects the company’s earned revenue that is still waiting to be collected, showing the fulfillment of the business’s side of a transaction while the customer’s payment is pending.
These accounts are recorded as a current asset on the balance sheet; they represent the total value of outstanding invoices.
What Is Accounts Receivable accounting?
Accounts receivable accounting is a subarea of financial accounting that records all business transactions with the company's customers (debtors).
Accounts receivable accounting deals with:
- The posting of receivables and credit notes from goods and services.
- Monitoring due dates and checking incoming payments.
- Dunning and collection.
- Classifying and checking debtor risk (creditworthiness).
Accounts Receivable Examples
Imagine you run a business that supplies parts to a computer manufacturer. A customer orders components worth $5,000, and you deliver them as agreed. You then send an invoice giving the customer 30 days to pay.
Even though you haven’t received the cash yet, the sale is already counted as income. The $5,000 is recorded as a customer balance owed to your business and is listed under accounts receivable until payment is received.
Once the customer pays the invoice, the receivable is cleared. The accounts receivable balance decreases by $5,000, and your cash balance increases by the same amount.
Now consider a different situation: the customer pays long after the invoice was due, and the amount had previously been written off as uncollectible. In this case, the transaction must be reinstated. You do this by restoring the $5,000 to accounts receivable and recognizing the income again by crediting revenue for the same amount.
Is Accounts Receivable an Asset?
Yes, accounts receivable are an asset because they represent money the business expects to receive from its customers, which provides economic benefits and supports the company’s financial position.
Assets are resources a company owns that provide economic benefits and support its financial position over time.
From an accounting perspective, accounts receivable are classified as current assets because they are expected to be converted into cash within a year. Current assets are the resources a business uses to meet its short-term obligations and support everyday operations. Typical examples include cash, inventory, and short-term investments.
Accounts Payable VS Accounts Receivable
A business maintains accounts receivable as the amount of money that customers and other debtors need to pay for delivered products and services. A business must pay its suppliers through accounts payable because it received goods and services but has not made payment yet.
The accounting system shows accounts receivable as a current asset because it represents future cash flow, but accounts payable appear as a liability because they show the company's outstanding payment responsibilities.
The supplier maintains control of accounts receivable in a buyer–supplier relationship, but the buyer controls accounts payable. The furniture business should record unpaid customer payments for custom chairs sold on installment plans as accounts receivable.
The company records its debt to the lumber wholesaler for raw materials as accounts payable. The lumber wholesaler would treat the outstanding unpaid invoice as an account that falls under accounts receivable.
Company A records accounts receivable when it sends an invoice to Company B because it expects to receive payment, while Company B records the same amount as accounts payable until it makes the payment.

Enerpize Accounting Software simplifies the management of both accounts receivable and accounts payable and is suitable for small and medium-sized businesses as well as large enterprises.
Importance of Accounts Receivable for Business
Understanding the Financial Condition
A business needs accounts receivable to understand its financial condition and perform effective financial management.
Measuring Liquidity
The measurement of liquidity requires accounts receivable because this account shows the amount of money that will enter the company's cash flow during the upcoming period.
Managing Working Capital
Accounts receivable enables businesses to manage their working capital effectively by providing access to business resources that become available after customers pay their debts.
Supporting Financial Forecasting
Financial forecasting requires accurate accounts receivable documentation because improper recording of these assets would make the balance sheet show incorrect current assets and prevent a complete financial presentation.
Standard Business Operating Procedure
Most businesses operate with a standard procedure that involves providing products or services before they send customers an invoice that shows when payment becomes due.
Handling Large Orders
The process of large order fulfillment requires customers to provide security deposits, but they do not need to pay the entire amount right away.
Cash Flow Challenges
The payment schedule of customers creates cash flow problems because they do not always pay their bills on time, which affects small businesses that depend on a few customers.
Monitoring Outstanding Debts
The process requires constant observation of outstanding debts together with their corresponding payment sources.
Improving Collection Processes
Businesses can monitor their outstanding invoices, contact customers, and make prompt collections of late payments through their accurate accounts receivable documentation system.
Enhancing Cash Flow and Customer Relationships
Companies that implement proper accounts receivable management will achieve better cash flow while they simplify their billing operations and payment systems and build stronger customer relationships.
Enerpize ERP system enables businesses to manage all accounts receivable activities easily and automatically through one integrated system. It helps track invoices, monitor outstanding balances, and support accurate financial reporting while improving cash flow and working capital management. By automating billing and collections, Enerpize reduces errors and strengthens customer relationships.
How to Calculate Accounts Receivable?
The total amount that customers owe to a company for delivered goods and services makes up the accounts receivable balance. Calculating accounts receivable requires adding all current customer invoices at a particular time and then subtracting all received customer payments.
Financial forecasting and modeling require the use of Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) to estimate accounts receivable because this metric connects receivables directly to revenue. The method shows the typical duration that businesses need to receive customer payments and enables them to predict their accounts receivable levels through sales performance evaluation.
Formula:
Accounts Receivable = (Days Sales Outstanding ÷ 365) × Revenue
The evaluation of accounts receivable performance requires three essential metrics, which are outlined below:
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
The accounts receivable turnover ratio shows the number of times accounts receivable are converted into cash during a specific period. A higher ratio indicates more efficient collection of customer payments.
Formula:
Accounts Receivable Turnover = Net Credit Sales ÷ Average Accounts Receivable
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO)
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) measures the average number of days a business takes to collect payment from customers. Lower DSO values suggest faster collections and improved cash flow.
Formula:
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) = (Average Accounts Receivable ÷ Net Credit Sales) × Number of Days
Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC)
The cash conversion cycle extends the analysis by measuring the total time required for a business to convert cash into inventory and then back into cash through sales and the collection of accounts receivable. A shorter CCC reflects stronger operational and financial efficiency.
Formula:
Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) = DSO + Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) − Days Payable Outstanding (DPO)
Where:
DIO = (Average Inventory ÷ Cost of Goods Sold) × Number of Days
DPO = (Average Accounts Payable ÷ Cost of Goods Sold) × Number of Days
Businesses can evaluate their accounts receivable operations using these metrics to identify performance gaps and implement improvements that enhance collection speed and overall financial stability.
Download our free accounts receivable template
Using Enerpize simplifies accounts receivable management by automating invoice tracking, calculations, and key metrics like DSO, turnover ratio, and CCC. This helps businesses monitor cash flow easily, reduce errors, and improve collection efficiency.
How to Reconcile Accounts Receivable?
Accounts receivable reconciliation is the process of verifying that the total amount recorded in the general ledger matches the sum of the balances of all customer accounts and related records. It helps ensure everything adds up and that the numbers accurately reflect what customers owe.
This process typically involves the following steps:

1- Review the accounts receivable ledger
Start by obtaining the accounts receivable balance from the general ledger for the reconciliation period.
2- Compare with the customer subledger
Add up all outstanding balances from individual customer accounts and verify that the total matches the general ledger balance.
3- Check outstanding invoices
Review all open invoices to ensure they are accurate, properly recorded, and reflect the correct amounts and due dates.
4- Verify incoming payments
Match customer payments received (such as bank deposits or receipts) to the corresponding invoices to confirm they have been correctly applied.
5- Investigate discrepancies
Identify and resolve differences caused by timing issues, posting errors, unapplied payments, credit notes, or write-offs.
6- Adjust and document corrections
Make the necessary journal entries to correct errors and document the reconciliation for audit and reporting purposes.
Regular reconciliation of accounts receivable helps ensure accurate financial records, improves cash flow management, and reduces the risk of errors or fraud.
How do You Record Accounts Receivable?
Accounts receivable are recognized when a business supplies goods or services without immediate payment and sends an invoice to the customer. These transactions are tracked and organized within individual customer accounts in the accounts receivable ledger.
When the invoice is issued, the customer’s receivable balance is increased, and revenue is recognized from the sale or service. The accounting entry for this is: Debit Accounts Receivable, Credit Revenue.
Next, the company monitors all incoming payments and matches them with the outstanding invoices. The accounts receivable balance is reduced as payments are received, with the corresponding entry being: Debit Cash (or Bank), Credit Accounts Receivable.
In some cases, payments may be unclear or unallocated. These are temporarily recorded in a clearing account until the correct customer account is identified and the payment is reassigned. When it becomes clear that a customer won’t be able to pay, the account is removed from the books and treated as a loss, according to the company’s bad debt policy.
This method ensures that all outstanding invoices are accurately documented and payments are properly tracked, so that the company’s accounts reflect the true accounts receivable balance. This, in turn, supports effective cash flow management and ensures accurate financial reporting.
Example: A company provides services worth $5,000 on credit to a customer. The customer pays $3,000 later. The remaining $2,000 cannot be collected and is written off as a bad debt.
| Description | Journal Entry | Accounts Receivable Balance | Cash/Bank Balance |
| Issue an invoice for $5,000 | Debit Accounts Receivable 5,000 Credit Revenue 5,000 | 5,000 | 0 |
| Receive partial payment $3,000 | Debit Cash (Bank) 3,000 Credit Accounts Receivable 3,000 | 2,000 | 3,000 |
| Write off bad debt $2,000 | Debit Bad Debt Expense 2,000 Credit Accounts Receivable 2,000 | 0 | 3,000 |
What is the Accounts Receivable Process?
The AR process covers all steps a business takes to manage customer payments, from delivery of a product or service through receipt of payment to account closure. It helps companies to track customer balances, follow up on unpaid balances, and maintain healthy cash flow and financial stability.
Accounts Receivable Process Steps:
- Providing goods or services on credit: The process begins when a business provides goods or services on credit and issues an invoice to the customer with agreed-upon payment terms.
- Issuing the invoice: The invoice amount is recorded in the accounts receivable ledger under that customer’s account.
- Recording in the ledger: The invoice amount is recorded in the accounts receivable ledger under that customer’s account.
- Monitoring due dates and incoming payments: The company monitors due dates and incoming payments to ensure collections stay on track.
- Applying received payments: When a payment is received, it’s applied to the correct invoice, reducing the outstanding balance.
- Handling unmatched payments: If a payment can’t be matched immediately, it’s temporarily placed in a clearing account until it can be assigned appropriately.
- Follow-up on missed payments: If a customer misses a payment deadline, the company begins follow-up actions, such as reminders or collection efforts, to encourage payment.
- Assessing debtor risk: Companies assess debtor risk by reviewing customers’ payment history and creditworthiness to minimize the risk of bad debts.
- Analyzing and reporting information: Relevant information on receivables and payment behavior is analyzed and reported to management or controlling, enabling informed operational and strategic decisions.
Overall, the accounts receivable process goes beyond simple bookkeeping and plays a key role in effective cash flow management and financial planning.
How to Manage Accounts Receivable Effectively?
Efficient accounts receivable management is essential for maintaining healthy cash flow and reducing payment delays. The following tips highlight practical ways to improve your receivables process:
1- Move to digital invoicing and online payments
Replace paper invoices and manual payments with electronic billing systems that allow customers to pay online quickly and securely. Integrated systems reduce errors and automate payment tracking.
2- Track key performance indicators (KPIs)
Monitor metrics such as Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), Average Days Delinquent (ADD), accounts receivable turnover, and collection effectiveness to assess and improve collection efficiency.
3- Standardize billing procedures
Document clear billing rules, invoice requirements, and follow-up processes to ensure consistency and accuracy across the organization.
4- Set clear credit and collection policies
Define credit terms in advance and apply structured, proactive collection practices to address overdue payments early.
5- Be proactive with collections
Contact customers as soon as payments are overdue and use automated reminders to maintain timely and professional communication.
6- Automate routine tasks
Use accounts receivable software to automate invoicing, reminders, and payment confirmations, allowing teams to focus on exception handling and customer relationships.
7- Simplify the payment experience
Make it easy for customers to pay by offering clear invoices, online payment options, and centralized payment portals.
8- Involve multiple teams
Encourage collaboration between finance, sales, and customer-facing teams to improve communication, identify issues early, and ensure faster cash collection.
What is Accounts Receivable Financing?
Accounts receivable (AR) financing is a funding solution that allows a business to access cash by using a portion of its unpaid customer invoices. Instead of waiting for customers to pay, the company receives immediate funds based on the value of those outstanding receivables. This type of financing can be structured either as a loan or through the sale of receivables, depending on the agreement.
In simple terms, AR financing works like a credit facility secured by the money the business expects to receive from its customers. It helps companies free up cash that would otherwise remain tied up in unpaid invoices, improving short-term liquidity and supporting day-to-day operations.
The amount of funding available depends on the size of the company’s accounts receivable balance. These receivables represent payments owed for goods or services delivered and are recorded as assets on the balance sheet.
Accounts receivable arise because many businesses offer credit terms to their customers. This may include invoicing regular clients periodically or allowing customers to pay after services are provided. The more a company relies on credit sales, the larger its receivables balance becomes, which in turn increases the potential funding available through AR financing.
How Enerpize Streamlines Accounts Receivable Management?
Enerpize online accounting software helps businesses manage accounts receivable efficiently and simply. By using the system, companies can issue electronic invoices and keep all customer billing information organized in one place. This accounts receivable automation makes it easier to track outstanding amounts and know precisely what customers owe and when payments are due.
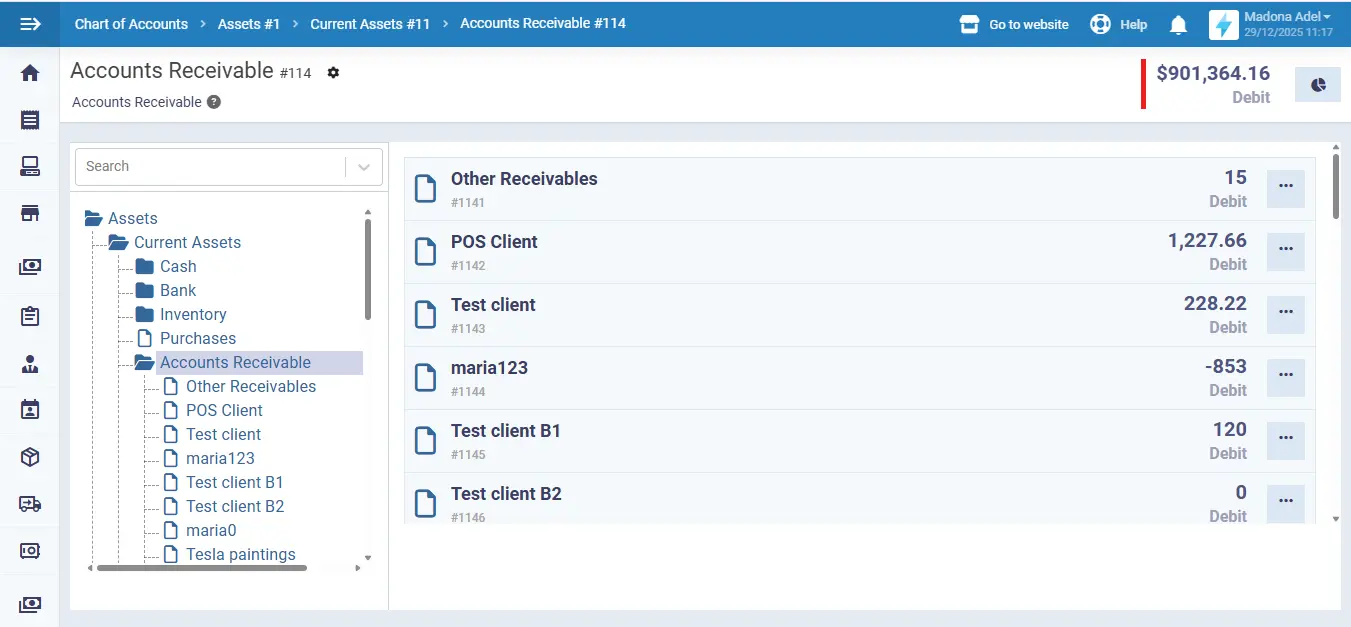
The software also supports recording and matching incoming payments with the correct invoices. Once a payment is received, it can be registered in the system and automatically reflected in the customer’s balance. This reduces manual work, minimizes errors, and ensures accounts receivable records remain accurate and up to date.
Enerpize allows businesses to manage customer accounts centrally. For each customer, you can view invoice history, outstanding balances, and payment status at any time. This gives a clear overview of receivables and helps finance teams follow up on overdue payments more effectively.
In addition, the system provides detailed financial reports related to sales, collections, and customer balances. These reports help businesses analyze their accounts receivable performance, monitor cash flow, and make better financial decisions. Overall, Enerpize supports better control, visibility, and efficiency in managing accounts receivable.
FAQs
Is accounts receivable a debit or credit?
Accounts receivable is recorded as a debit. When a company issues an invoice for goods or services provided on credit, accounts receivable is debited to reflect the amount owed by the customer. When the customer pays, accounts receivable is credited, reducing the balance.
Is accounts receivable a current asset?
Yes, accounts receivable is classified as a current asset.
It represents amounts that a company expects to collect from customers within a short period, typically within one year, making it part of the company’s short-term assets.
What type of account is accounts receivable?
Accounts receivable is an asset account, specifically a current asset account on the balance sheet.
It reflects the company’s legal claim to receive cash from customers for goods or services already delivered.
What does accounts receivable do?
Accounts receivable refers to the amounts customers still owe for goods or services already provided. It allows businesses to track unpaid invoices, manage incoming payments, plan cash flow, and assess customer reliability. Properly managing accounts receivable helps ensure timely payments and supports overall financial health.

In summary, accounts receivable are a crucial part of any business’s financial management. By effectively tracking customer payments, managing outstanding invoices, and assessing credit risk, companies can maintain healthy cash flow and ensure financial stability.
Using the right processes and tools, like digital invoicing and accounting software, makes managing receivables simpler, more accurate, and more efficient, supporting the overall growth and success of the business.
Managing accounts receivable is easy with Enerpize.
Try Enerpize accountig software to manage accounts receivable automatically.