Author : Haya Assem
Reviewed By : Enerpize Team
Journal Entries in Accounting: Definition, Format, and Types

Table of contents:
- What is a Journal Entry?
- What to Include in a Journal Entry?
- What is Not Included in a Journal Entry?
- Journal Entries Examples
- What are The Types of Journal Entries?
- How to Prepare Journal Entries?
- Journal Entry Format
- What is the Accounting Purpose of Journal Entries?
- Recording Journal Entries Tips and Tricks
- What is the Easiest Way to Understand Journal Entries?
- How to Do a Write-Off Journal Entry?
- What is the Basic Journal Entry Rule?
- How to Track Journal Entries?
- What Is Debit and Credit in Journal Entry?
- Automate your Journal Entries with Enerpize!
- FAQs About Journal Entries
Journal entries are the backbone of any accounting system, playing a crucial role in documenting every financial transaction with precision. Whether recording revenues, expenses, or asset movements, journal entries ensure that financial data remains structured and reliable.
Using the double-entry accounting system, they maintain the balance of the accounting equation, preventing errors and enhancing financial transparency. Properly recording journal entries is essential for generating accurate financial reports, complying with accounting standards, and making informed business decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Journal entries are critical in accounting for documenting all business activities and tracking financial operations, and they use the double-entry approach to ensure accuracy and balance.
- They record transactions accurately, including reference numbers, dates, descriptions, impacted accounts, and debit/credit amounts for clarity and recognition.
- Journal entry types: Opening (start of period), Transfer (move between accounts), Compound (multiple transactions), Closing (period end), Adjusting (end adjustments), Reversing (simplify next period).
- Essential steps in journal entry preparation: Organize transaction documents, identify affected accounts, determine debit/credit entries, generate entries with date and description, and close temporary accounts for accurate financial records.
- Journal entries crucially document financial transactions, applying a double-entry system for integrity. They form the basis for ledgers, aiding compliance, and are vital for financial statements and auditing accuracy.
- For an accurate tracking of journal entries choose a suitable system, categorize expenses, reconcile regularly with bank statements, and secure digital data.
What is a Journal Entry?
A journal entry is the foundational record in accounting that documents every financial transaction of a business. It represents the first step in the accounting cycle, ensuring accuracy and reliability in the way transactions are captured.
Each entry records the date of the transaction, the accounts affected, the debit and credit amounts, along with a brief description and reference number.
By following the double-entry system, journal entries keep the accounting equation in balance and provide a structured record that supports transparency and consistency in financial reporting.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
What to Include in a Journal Entry?
A journal entry requires a few elements to be included in order to reflect and recognize the transaction accurately. The elements of a journal entry are:
Reference number: Unique identifier or reference no. to retrieve the entry when required.
Date: The date when the transaction took place.
Description: A brief description of the transaction’s details.
Accounts: Impacted account names or numbers.
Amounts: Debit and Credit amounts involved in the transaction.
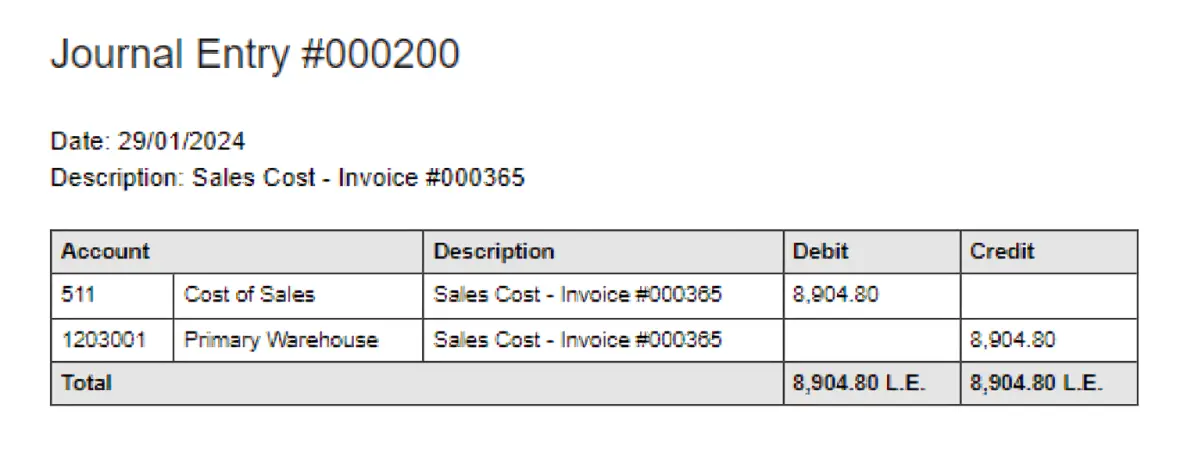
What is Not Included in a Journal Entry?
Although a journal entry mostly captures all essential details of a financial transaction, it does not include some business operations information. Information excluded from a journal entry includes:
- Supporting documents, such as invoices, receipts, or contracts, they are kept separately as proof but are not part of the entry itself.
- Personal notes or comments that are not directly tied to the transaction.
- Future estimates or projections. Only actual, measurable transactions are recorded.
- Non-financial data, such as operational details or management decisions, that fall outside the accounting system.
Journal Entries Examples
Simple Journal Entries
A simple journal entry involves only one account being debited and one account being credited.
Example 1
A company purchases 100 printers on credit for $10,000. The total amount owed to the supplier is $10,000, recorded on the accounts payable.
- Debit: Inventory $10,000
- Credit: Accounts Payable $10,000
Journal Entry
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
| 20/12/2024 | Inventory | $10,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | $10,000 |
Example 2
A Consulting completed a $1,200 consulting project for a client on December 29, 2024. The client will pay within 30 days. Since the service has been completed, the company records the revenue, even though payment has not yet been received.
- Debit: Accounts Receivable $1,200
- Credit: Service Revenue $1,200
Journal Entry
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
| 20/11/2024 | Account Receivable | $1,200 | |
| Service Revenue | $1,200 |
Compound Journal Entries
A compound journal entry is a type of journal entry that involves more than one debit and/or credit.
Example
A purchases raw materials worth $5,000 on credit, and also incurs a $300 delivery charge for bringing the materials to the factory. The company received an invoice for the total amount, which is $5,300. The payment will be made at a later date.
- Debit: Raw Materials Inventory $5,000
Delivery Expense $300
- Credit: Accounts Payable $5,300
Journal Entry
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
| 29/12/2024 | Raw Materials Inventory | $5,000 | |
| 29/12/2024 | Delivery Expense | $300 | |
| 29/12/2024 | Accounts Payable | $5,300 |
If you want to start with a simple journal entry, download our journal entry template for free!
What are The Types of Journal Entries?
Journal entries can be categorized into several types based on the nature of the transaction or event being recorded.
1- Compound entries
A compound entry involves more than two accounts and is used when multiple transactions are recorded in a single entry, and they may not follow the strict one-to-one rule of journal entries. For example, a single entry may involve both revenue and expense accounts.
2- Closing entries
Closing entries are made at the end of an accounting period to close temporary accounts (revenue, expense, and dividend accounts) and transfer their balances to the retained earnings or owner's equity account.
3- Reversing entries
Reversing entries are made at the beginning of an accounting period to reverse adjusting entries made in the previous period, simplifying the accounting process for certain transactions.
4- Adjusting entries
Adjusting entries are made at the end of an accounting period to adjust account balances for accruals, deferrals, depreciation, and other adjustments necessary to reflect the business's financial position accurately.
5- Opening entries
A current accounting period's opening entry is the preceding accounting period's closing balance. Recorded at the beginning of an accounting period to open various temporary accounts and establish account balances for the period.
6- Transfer entries
It is an entry that records transactions from one account to another within the same organization. It involves debiting one account and crediting another account to reflect the incoming transfer.
7- Payroll journal entries
Payroll journal entries record wages, salaries, taxes, and benefits related to employee compensation. For example, a payroll journal entry might debit the "Wages Expense" account and credit the "Cash" or "Payroll Liabilities" accounts (such as "Payroll Taxes Payable" and "Employee Benefits Payable").
8- Revenue journal entries
These entries are made to record income from business operations such as sales of products and services. These entries usually involve debiting the "Accounts Receivable" (or "Cash") account and crediting a "Revenue" account (like "Sales Revenue").
Related reads you might find helpful: Sales Journal Entries: Examples and How to Record
9- Purchase journal entry
This entry is used to record purchases of products or services on credit. It generally involves debiting the "Inventory" (or "Expense") account and crediting the "Accounts Payable" account to reflect the liability incurred for the purchase.
10- Prepaid Expense Journal Entries
Prepaid expenses are costs that have been paid in advance, such as insurance or rent. Prepaid expense journal entries usually involve debiting a prepaid expense asset account (e.g., "Prepaid Insurance") and crediting "Cash" or "Bank" to reflect the payment.
11- Intercompany transactions journal entries
Intercompany transactions journal entries record transactions between different subsidiaries or entities within the same parent company. These might involve debiting an account for one subsidiary and crediting a corresponding account for the other, such as transferring products, services, or loans between subsidiaries.
12- Lease accounting journal entries
Lease accounting journal entries are used to record the financial impact of leases. Under IFRS or GAAP, this may involve recording a "Right-of-Use Asset" and a corresponding "Lease Liability" when a lease is initiated. Payments made to leaseholders are recorded as debits to the lease liability and credits to cash.
How to Prepare Journal Entries?
Preparing journal entries is an essential process in the field of accounting, as it plays a critical role in maintaining exact and comprehensive financial records for any organization. In the following lines, you will find accurate guidance for creating a journal entry.
.png)
1- Keep all invoices and documents related to all business transactions
Before creating a journal entry, it is essential to keep a detailed record of all business transactions. This entails meticulously gathering and categorizing invoices, receipts, and other relevant documents from all transactions. These records serve as the foundation for accurate financial reporting.
2- Determine the affected accounts
Once all necessary documents are in order, the next step is to analyze the transactions and determine which accounts are impacted. This entails identifying specific assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, or expenses that are influenced by the business operation or transaction in question.
3- Identify debit and credit accounts
The following step is to understand the nature of the transaction and the accounting rules associated with it in order to determine which accounts will be debited or credited such as revenue, expenses, liabilities, and assets.
4- Start preparing the journal entry
After identifying the impacted accounts and determining the debits and credits, you can start generating the journal entry.
Start by entering the transaction's date, recording debits and credits into the relevant accounts, and adding the transaction's unique number, which will help you to track transactions more easily. Also, add a brief description of the transaction with exact amounts.
5- Close your accounting entries
At the end of each accounting period, it is necessary to close temporary accounts such as revenue and expenses. Closing entries reset these accounts to zero, preparing them for the next accounting period.
This involves transferring the journal entries to a general ledger. The process ensures that the financial records accurately reflect the company's performance and position during a certain time period.
Read Also: How to Do Journal Entries: A Comprehensive Guide

Journal Entry Format
The journal entry format includes the date of the transaction, the accounts involved, and the corresponding debit and credit amounts.
The format begins with the date when the transaction occurred, followed by the names of the accounts that are affected.
The account(s) being debited are listed first, followed by the account(s) being credited. The debit and credit amounts must always be equal, ensuring the transaction is balanced.
This format ensures that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) remains in balance. A journal entry format is as follows:
| Date | Account | ($) Debit | ($) Credit |
| DD/MM/YY | Account Debited | Amount | |
| DD/MM/YY | Account Credited | Amount |
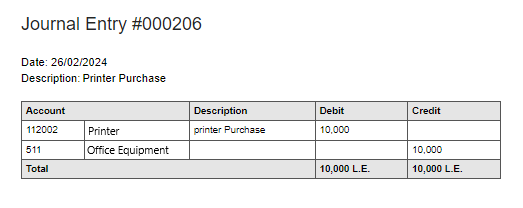
What is the Accounting Purpose of Journal Entries?
The primary accounting purpose of journal entries is to record and organize every financial transaction in a business accurately. Journal entries act as the foundation of the accounting process by ensuring that all transactions are documented with their corresponding debit and credit accounts.
This keeps the accounts in balance and builds a timeline of transactions that can be reviewed anytime.
Through this role, journal entries help businesses:
- Keep financial records accurate, consistent, and reliable.
- Ensure transparency and provide clear evidence during audits.
- Monitor and trace the cash flow across different accounts.
- Build ledgers that form the foundation for better financial statements.
Recording Journal Entries: Tips and Tricks
Recording journal entries is a fundamental part of accounting, ensuring that all financial transactions are accurately documented. Here are some essential tips and tricks to help you maintain error-free journal entries.
Follow the Double-Entry Rule
Every transaction must have at least one debit and one credit entry, ensuring that the accounting equation remains balanced.
Use Clear and Consistent Account Titles
Always use the correct account names (e.g., "Accounts Receivable" instead of "Customer Payment") to avoid confusion in financial reports.
Record Transactions Immediately
Delaying entries can lead to missing or incorrect records. Make it a habit to record transactions as soon as they occur.
Maintain Supporting Documents
Attach invoices, receipts, or contracts to journal entries to provide proof and facilitate audits.
Double-Check Debit and Credit Amounts
Errors in the debit and credit columns can result in an unbalanced ledger. Always review calculations before finalizing entries.
Categorize Expenses and Revenues Properly
Ensure that expenses and revenues are assigned to the right accounts to maintain accurate financial statements.
Review and Reconcile Regularly
Periodically reviewing journal entries and reconciling accounts helps detect errors early and ensures financial accuracy.
What is the Easiest Way to Understand Journal Entries?
The simplest way to understand journal entries is to see them as a record of how cash moves within a business.
Each transaction has two sides: a debit (where the value goes) and a credit (where the value comes from). By linking these two sides, journal entries provide a complete view of the financial impact of every transaction, ensuring both clarity and balance in the accounts.
How to Do a Write-Off Journal Entry?
A write-off journal entry is used when a business determines that a receivable or asset no longer holds value and should be removed from the accounts.
For instance, when writing off a bad debt, the entry typically involves debiting Bad Debt Expense (to recognize the loss) and crediting Accounts Receivable (to remove the uncollectible balance). This process ensures that the financial statements reflect only collectible assets and present a more accurate view of the company’s financial position.
What is the Basic Journal Entry Rule?
The basic rule of journal entries is simple:
- Debit what comes in (assets and expenses).
- Credit what goes out (liabilities, equity, and revenue).
This ensures that the accounting equation we mentioned before (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) always stays balanced.
How to Track Journal Entries?
First, identify a system that is suitable for your business. This may be done using spreadsheets or accounting software like Enerpize. Categorize each expense, create subcategories, and ensure the transaction details are recorded accurately.
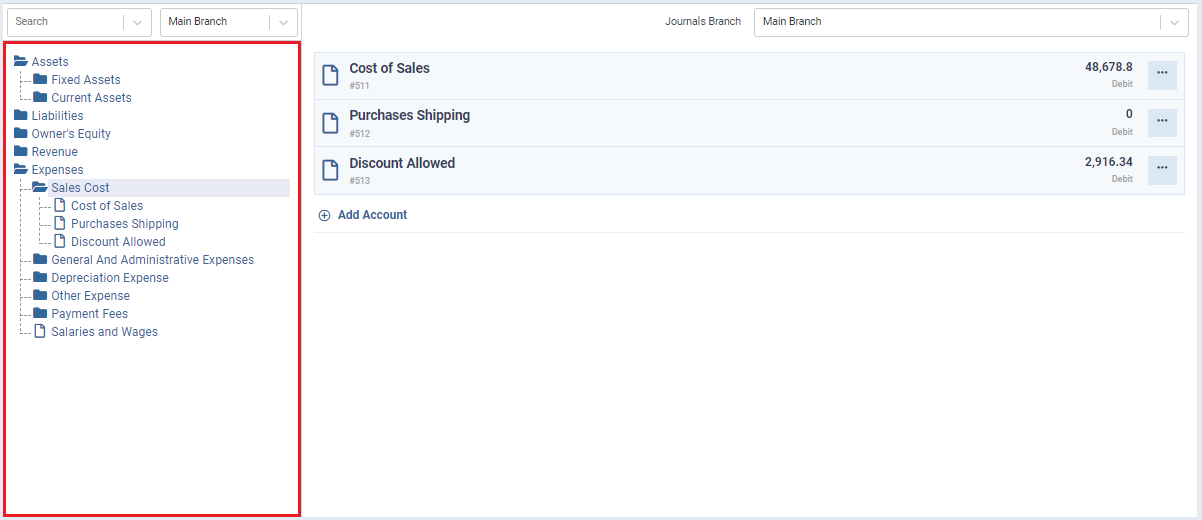
Additionally, regular account reconciliation is required. The process involves comparing your recorded transactions to bank statements to ensure accuracy and detect and correct any discrepancies.
For more about the bank reconciliation process, read our blog: Journal Entries for Bank Reconciliation: A Comprehensive Guide.
Use cloud-based software to securely save digital data for the possibility of a disaster, such as a hard drive failure or theft. By following these tips, you will be able to keep track of your journal entries in an organized and efficient way.
What Is Debit and Credit in Journal Entry?
Debits and credits are the foundation of the double-entry accounting system, ensuring that every financial transaction is properly recorded and balanced. Each transaction affects at least two accounts: one account is debited, and another is credited, keeping the accounting equation intact:
Assets= Liabilities + Equity
Debits (Dr)
- Increase assets and expenses
- Decrease liabilities, equity, and revenue
Credits (Cr)
- Increase liabilities, equity, and revenue
- Decrease assets and expenses

Automate your Journal Entries with Enerpize!
Much effort is frequently wasted revising entries, inputting daily transactions, and transferring them to the general ledger, which is a long and complex process. This is something Enerpize saves you from.
Enerpize's online accounting software creates entries as soon as a transaction occurs in the system. It also automatically balances these transactions in the account ledger before transferring them to the general ledger for inclusion in the trial balance.
Furthermore, it includes them in the financial statements and reports. This saves you a lot of time and effort and also streamlines the work for the accounting team.
FAQs About Journal Entries
What are the two main types of journal entries?
The two primary types are simple journal entries (involving one debit and one credit) and compound journal entries (involving multiple debits and/or credits).
What goes first in a journal entry: debit or credit?
Debits are always listed first, followed by credits.
Should journal entries always balance?
Yes. The total debits must always equal the total credits in every journal entry.
What is the difference between journal entries and journal proper?
A journal entry is the act of recording a transaction, while the journal proper is the main book where all entries are recorded chronologically.
How do I lay out journal entries?
You can follow this detailed guide for step-by-step instructions on structuring your entries.
What is considered a journal entry?
A journal entry is the official record of a financial transaction in the books of accounts.
What is the basic concept of a journal entry?
Every transaction must affect at least two accounts, following the double-entry accounting principle.
Why do we prepare a journal entry?
Journal entries provide a clear, chronological record of all business transactions, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
What does a journal entry start with?
It begins with the date of the transaction, followed by the accounts involved.
What should a journal entry look like?
A standard entry includes the date, accounts debited and credited, amounts, and a brief description.
What is the structure of a journal entry?
- Date
- Debit account(s) with an amount
- Credit account(s) with an amount
- Narration or explanation
What are the three basic rules all journal entries must follow?
- Debit what comes in, credit what goes out.
- Debit expenses and losses, credit incomes and gains.
- Debit the receiver, credit the giver.
What are the four parts of a journal entry?
- Date
- Accounts involved
- Debit and credit amounts
- Description
What are the five steps to every journal entry?
- Identify the transaction.
- Analyze which accounts are affected.
- Determine debit and credit impact.
- Record the entry in the journal.
- Verify that debits equal credits.
What is the proper order when completing a journal entry?
Always record the date first, then debits, followed by credits, and end with a short narration.
Journal entries are easy with Enerpize.
Try our accounting module to mange your journal entries








