Author : Haya Assem
What Is Tax Liability: A Complete Guide

Table of contents:
Tax liability is the total amount of tax a business or individual owes to tax authorities, based on income, sales, payroll, or other taxable activities.
Understanding your tax liability is essential for financial planning, avoiding penalties, and staying compliant with the law. This article breaks down what tax liability means, its various types, how it’s calculated, and how to reduce it.
Key Takeaways
- Tax liability is the tax amount a business owes to the tax authorities or federal entities.
- Income tax, sales tax, payroll tax, and capital gains tax are common examples of tax liability.
- Tax liabilities can be immediate or deferred, depending on timing differences in reporting and payment.
- Proper calculation and timely payment help avoid penalties, interest, and legal consequences.
- Online accounting software can automate and simplify tax liability tracking and reporting.
What Is Tax Liability?
Tax liability refers to the amount of taxes a business owes to a government or federal entity. To better understand the term, it can be broken down into two parts:
- tax: which is the mandatory financial charge imposed on a business
- liability: which is a financial obligation or debt that a business is required to settle.
When combined, tax liability represents the total amount of tax debt that a company is obligated to pay to governmental authorities. It reflects the legal responsibility of the business to meet its tax obligations based on income, sales, payroll, or other taxable activities.
Types of Tax Liabilities
Tax liabilities can take different forms and often vary based on the nature of the business and its operations. The following are the most common types businesses may encounter:
- Income Tax Liability: Taxes owed on business profits.
- Sales Tax Liability: Taxes collected from customers on sales and owed to the government.
- Payroll Tax Liability: Taxes withheld from employee wages and employer payroll contributions.
- Property Tax Liability: Taxes due on owned real estate or business property.
- Capital Gains Tax Liability: Taxes on profits from selling business assets or investments.
Read Also: A Comprehensive Guide to Current Liabilities
Tax Liabilities Examples
To better understand how tax liabilities work in real-world situations, here are some practical examples of the most common types of tax liabilities:
Income Tax Liability
A business earns $100,000 in profit for the year. Based on the corporate income tax rate of 20%, it owes $20,000 in taxes to the government.
$20,000 is the income tax liability.
Sales Tax Liability
A retail company sells products worth $50,000 and collects 10% sales tax from customers. It collects $5,000 in tax.
This $5,000 must be paid to the tax authority and is recorded as a sales tax liability.
Enerpize invoicing software can automatically apply sales tax to invoices. After you set up sales tax, the system applies it to invoices whenever the “Sales Tax” option is selected.
Payroll Tax Liability
A company pays employees a total of $40,000 monthly. It withholds income tax and social security contributions (e.g., $6,000) from salaries and must also contribute employer taxes.
The owed amount and the employer’s share become a payroll tax liability.
Enerpize software makes it easy for businesses to calculate and manage different types of taxes, whether it’s income tax, sales tax, or payroll tax. The system automatically applies tax rates, tracks liabilities, and generates detailed tax reports, ensuring accuracy and compliance with local regulations.

What Are Federal Income Tax Liabilities?
Federal income tax liabilities refer to the amount of income tax a business or individual owes to the federal government based on their taxable income.
This liability is calculated per federal tax laws and must be reported and paid within specific deadlines, typically through annual tax returns or estimated tax payments.
Failure to pay federal income tax liabilities can result in penalties, interest, or legal action by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Read Also: What Are Contingent Liabilities in Accounting?
Deferred Tax Liabilities
Deferred tax liabilities are taxes a company owes but postpones paying to future periods. They arise due to temporary differences between financial statements and tax returns, often from depreciation methods or revenue recognition timing.
Although the tax isn’t due now, it represents a future obligation the company will eventually have to settle with the tax authorities.
Recommended for you: Long Term Liabilities In Accounting: Examples And How To Calculate
How To Calculate Tax Liabilities
Calculating your tax liability may seem complex, but it becomes manageable when broken into clear steps. Here's a simple breakdown of the process:
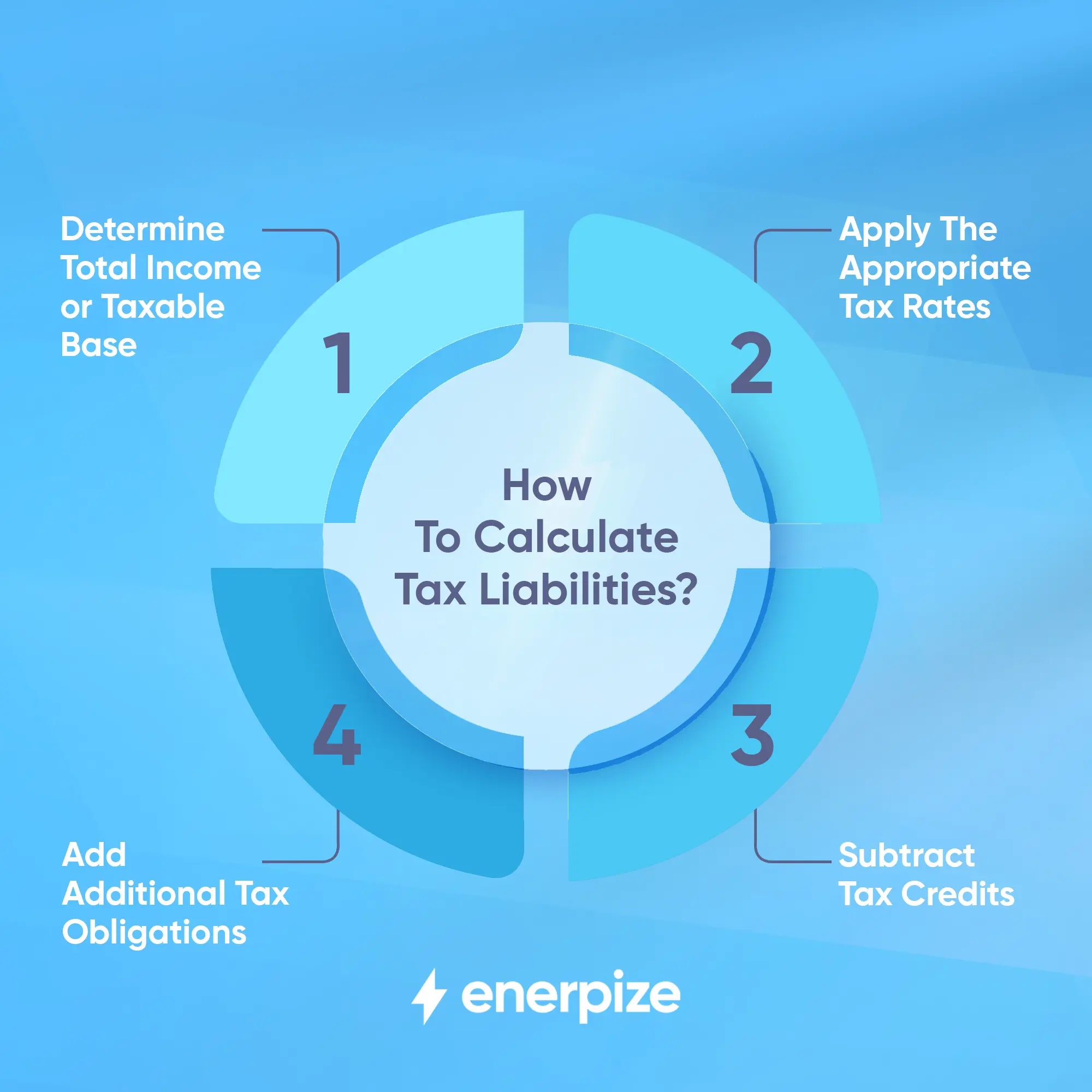
1- Determine Total Income or Taxable Base
First, compile all sources of income, salaries, wages, bonuses, dividends, capital gains, business income, etc., to arrive at your total gross income. Then subtract allowable deductions to calculate your taxable income (adjusted gross income less deductions).
Enerpize centralizes your income and expense records, allowing you to instantly generate an income statement that clearly shows the net profit, helping to confirm the taxable income before applying deductions.
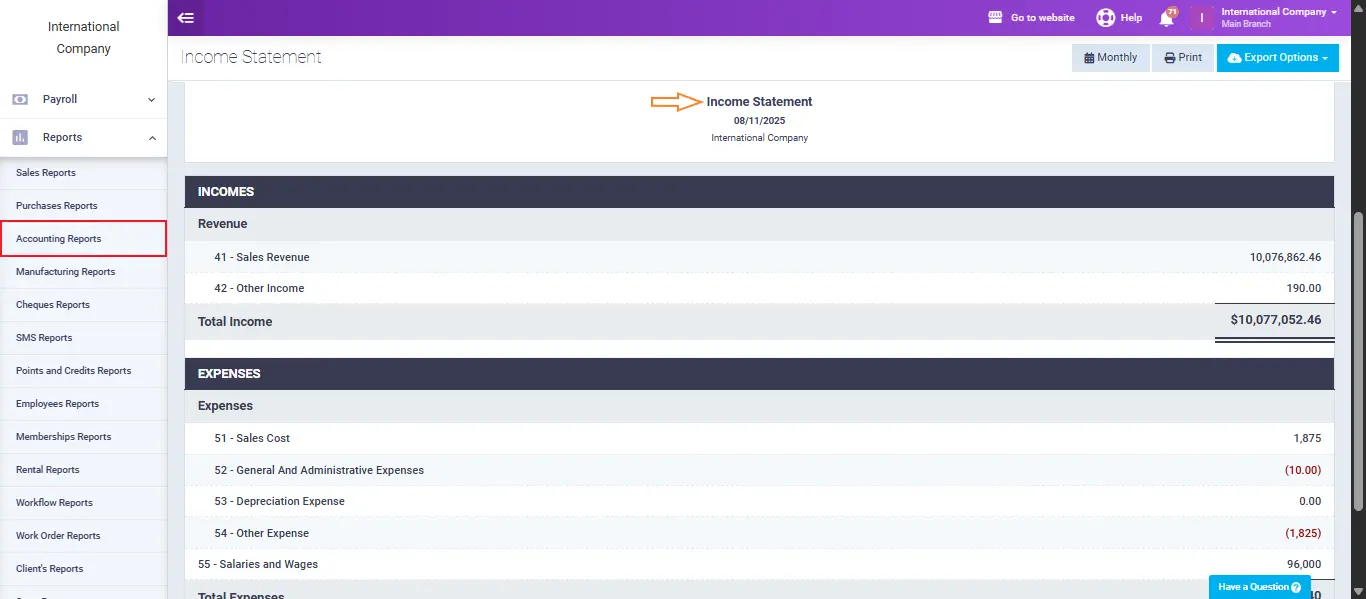
You can use: Google Sheets Income Statement Template
2- Apply the Appropriate Tax Rates
In a progressive tax system, taxable income is taxed across brackets. For example, income is taxed at 10% up to a threshold, then 12%, 22%, and so on as income rises. The tax owed is the sum calculated by applying each bracket’s rate to the income in that range.
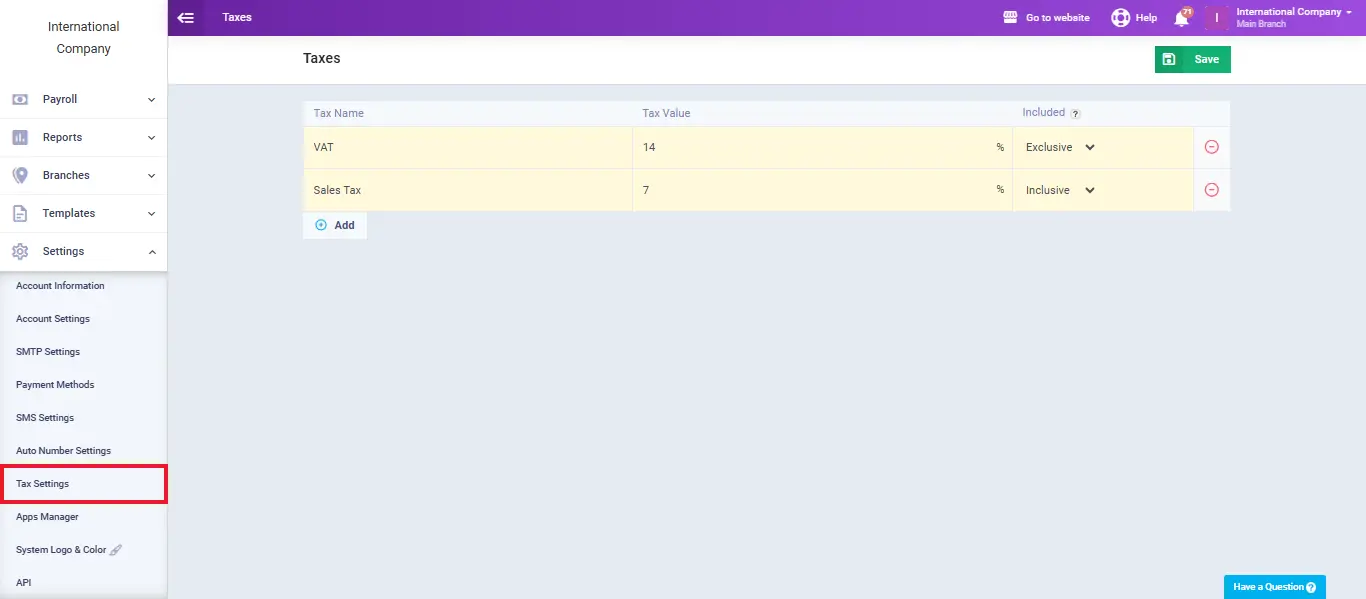
You can set up tax rates within Enerpize, which are then automatically applied to invoices and related transactions.
3- Subtract Tax Credits
After computing gross tax based on brackets, reduce that amount by any applicable tax credits, which directly lower your tax owed dollar-for-dollar, including education credits, child tax credit, or energy incentives.
4- Add Additional Tax Obligations
Include other taxes such as payroll taxes, self-employment taxes, alternative minimum tax (AMT), or deferred tax liabilities, if applicable.
Enerpize’s payroll module automatically records payroll-related liabilities and integrates them into your overall accounting records.
You may also like: How to Calculate Liabilities
How To Reduce Tax Liabilities
Businesses and individuals can reduce their tax liabilities legally by using various tax-saving strategies, such as:
Claim All Eligible Deductions
Make sure to deduct all allowable expenses related to your business or personal finances. These may include business costs, home office expenses, medical bills, or educational expenses, which can significantly lower your taxable income.
Explore more on this topic: How To Track Business Expenses
Utilize Tax Credits
Tax credits reduce your actual tax bill, not just your income. Credits such as the earned income tax credit, R&D credits, or energy efficiency incentives can directly lower the amount you owe.
Contribute to Retirement Plans
Contributions into retirement accounts like a 401(k) or IRA not only prepare you for the future but also reduce your current taxable income, helping lower your tax burden now.
Defer Income
If possible, you can delay receiving certain income until the next tax year. This strategy can be useful in managing your tax bracket and keeping your liability lower in the current year.
Use Depreciation Strategies
Businesses can take advantage of accelerated depreciation methods to write off the cost of assets more quickly, lowering taxable income in the earlier years of asset use.
Work with a Tax Professional
A qualified tax advisor can help you identify tax-saving opportunities, ensure compliance, and implement effective strategies tailored to your financial situation.

Recommended for you: What Is Accrued Liability for Small Business: A Detailed Guide
Streamline Tax Liabilities Calculating With Enerpize
Enerpize online accounting management software is designed to help businesses manage their operations efficiently. It offers integrated tools for accounting, invoicing, HR, inventory, and more, all in one centralized system.
Enerpize simplifies the process of calculating tax liabilities by automating tax calculations across income, sales, and payroll transactions. With built-in tax rules and customizable settings, the system ensures accuracy while minimizing manual errors.
Enerpize automatically tracks taxable income, applies the correct tax rates, and generates detailed reports, helping businesses stay compliant and save valuable time during tax seasons.
FAQs About Tax Liabilities
What Are Tax Liabilities on W-2?
Tax liabilities on a W-2 refer to the amount of federal, state, and other taxes withheld from an employee’s wages. It shows how much tax has been paid on your behalf and helps determine if you still owe taxes or are due a refund when filing your return.
What Are Tax Liabilities on W-4?
On a W-4 form, tax liabilities relate to how much tax you expect to owe for the year. The information you provide, such as dependents and other income, helps your employer calculate how much tax to withhold from your paycheck to cover that liability.
How Do I Know If I Have Tax Liabilities?
You can check your tax liability by reviewing your income, deductions, and tax payments. If the taxes you owe exceed what’s been paid or withheld, you have a tax liability. You can also verify this when filing your tax return or by checking your IRS account online.
What Happens If I Don't Pay Tax Liability?
If you don’t pay your tax liability, you may face penalties, interest charges, wage garnishments, or even legal action by tax authorities. It’s important to pay on time or arrange a payment plan with the IRS or your local tax agency.
Where Can I Find Tax Liabilities?
You can find your tax liabilities on your tax return summary, through IRS or local tax authority portals, or within accounting software like Enerpize that tracks and reports taxes owed for your business.
What Does Tax Liabilities Mean?
Tax liabilities refer to the total amount of taxes a person or business owes to the government. This includes income tax, sales tax, payroll tax, and other applicable taxes based on earnings or operations.
Do I Have Tax Liabilities?
If you earn income, sell taxable goods or services, or run a business, you likely have tax liabilities. The exact amount depends on your financial activity and the tax rules that apply to your situation.
What Are My Tax Liabilities?
Your tax liabilities include any unpaid taxes for the current or previous tax years. They can be calculated by totaling the taxes you owe after applying deductions, credits, and payments already made.
How Do I Know If I Have No Tax Liability?
You have no tax liability if your total tax owed is zero or if your tax credits and withholdings fully cover what you owe. This can be confirmed when filing your tax return or through your tax software/account.
Calculating tax liabilities is easy with Enerpize.
Try Enerpize accounting software to calculate tax liabilities accurately.








